Figure 7. The Sec31 binding site is proximal to the CLSD mutation and residues of Sar1 that differ between homologs.
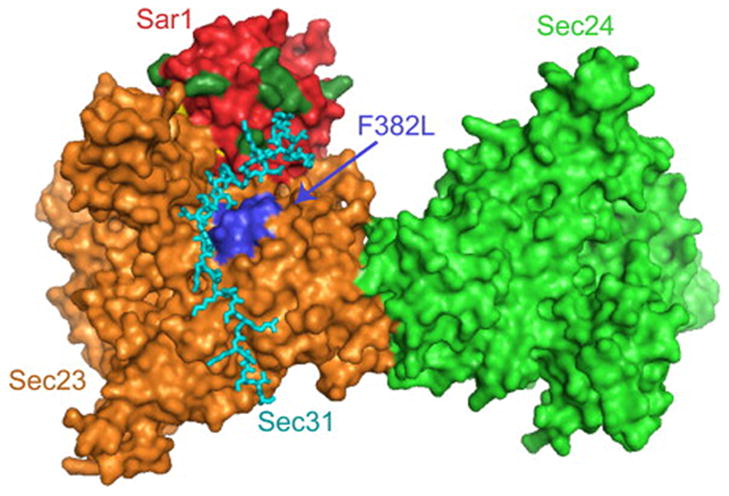
Atomic structure of a fragment of yeast Sec31 (cyan) in complex with Sar1p (red) and Sec23p (orange) (Bi et al., 2007), with Sec24p (light green) included based on the structure of the Sar1p-Sec23p-Sec24p pre-budding complex (Bi et al., 2002). The membrane binding surface of this complex is thought to lie underneath this perspective. The position of the yeast residue equivalent to human F382 (F380) is indicated by blue coloring of several residues surrounding position 380 in primary sequence, and by the label “F382L”. The eight residues of human Sar1 that are significantly different in chemical composition between SAR1A and SAR1B (as shown in Figure 1B) are highlighted in dark green. All eight of these residues lie on the globular surface of Sar1, and six of them are on the same face of the complex as is F380. In particular, residues corresponding to positions 80, 113, 116, and 117 in human Sar1 appear capable of making direct contact with Sec31.
