Fig. 1.
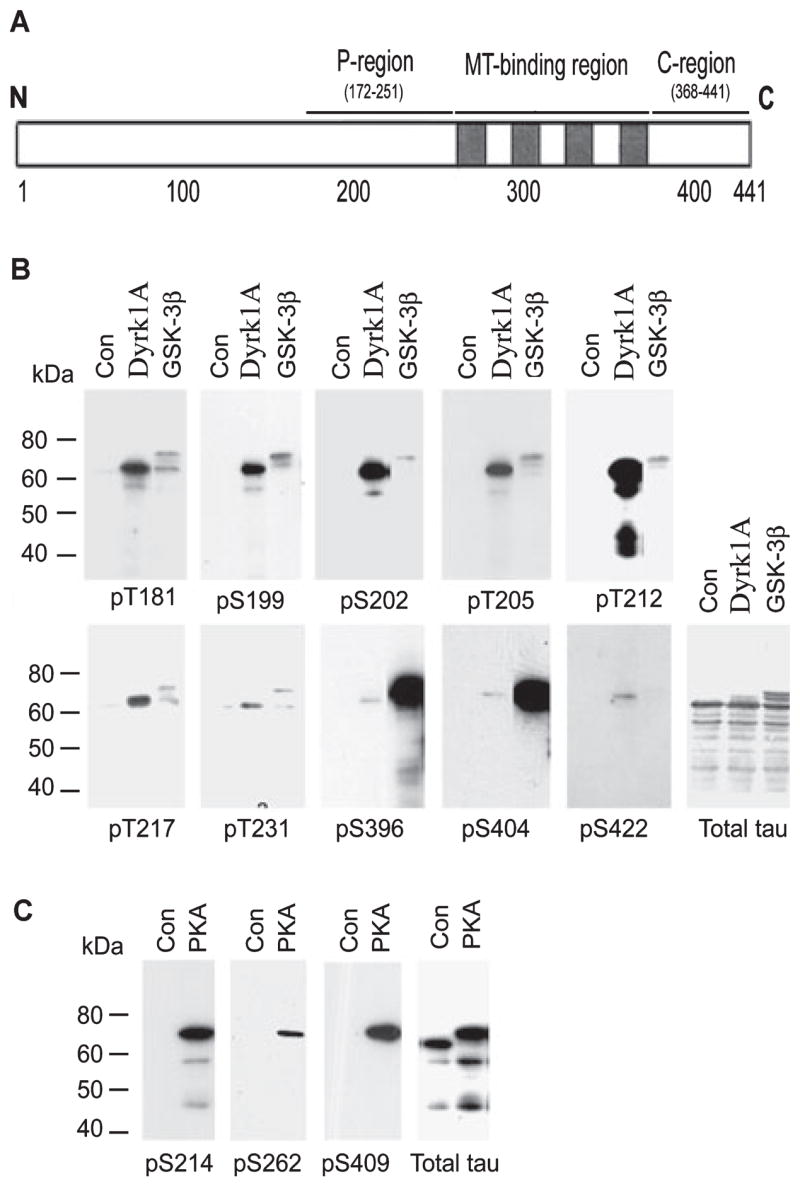
Site-specific phosphorylation of tau by dual-specificity tyrosine-phosphorylated and -regulated kinase 1A (Dyrk1A), glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) and cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA). (A) Schematic diagram of tau441, showing the proline-rich region (P-region), microtubule (MT)-binding region and C-terminal tail region (C-region), where the majority of the serine and threonine residues are phosphorylated in Alzheimer’s disease brain. (B and C) Recombinant tau441 was first phosphorylated in vitro to ~2.0 mol phosphates/mol tau by catalysis with Dyrk1A, GSK-3β or PKA. The phosphorylated tau and the control-treated tau (Con) were then subjected to western blots developed with antibodies recognizing total tau or tau phosphorylated at specific sites, as indicated under each blot.
