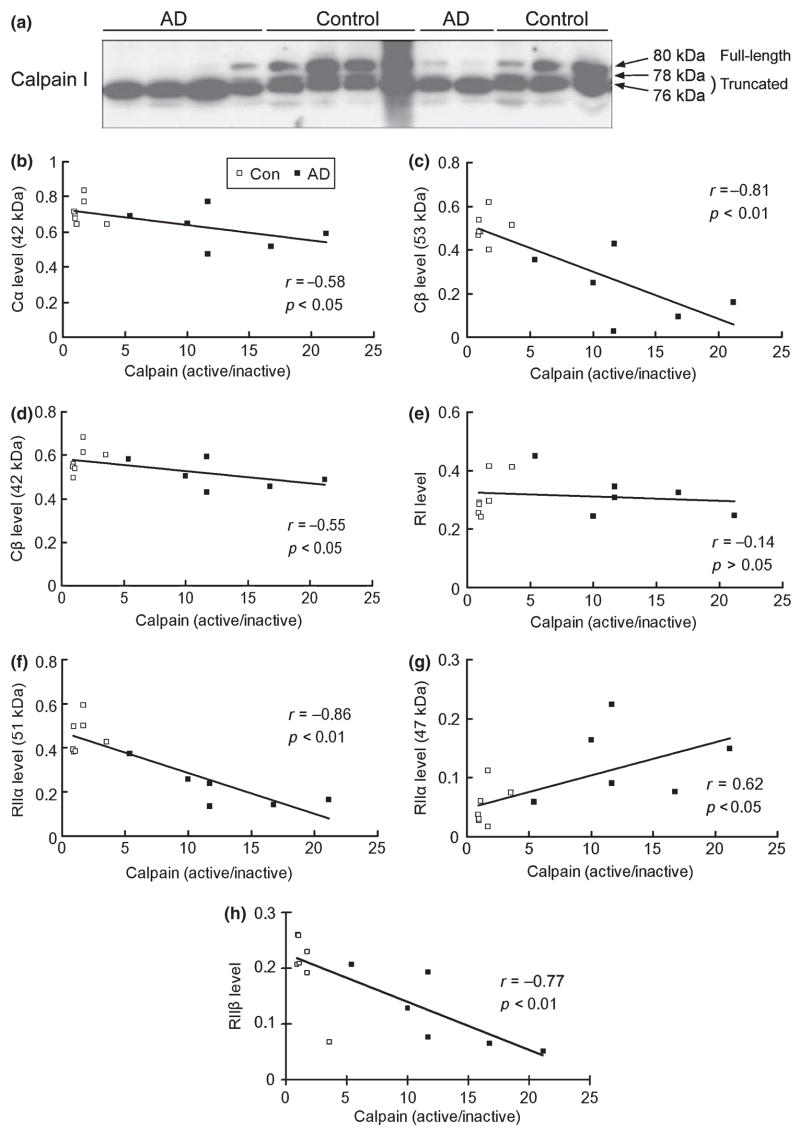
Fig. 5.
Correlation analysis between the levels of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) subunits/isoforms and calpain activation in human brain. (a) Western blots of calpain I of medial temporal cortical homogenate from six Alzheimer disease (AD) and seven control cases. The apparent molecular weights of the full length and the truncated calpain are marked on the right of the blot. (b–h) Linear correlation analyses between the levels of each PKA subunit/isoform and calpain activation in 13 human brains (six AD and seven controls).