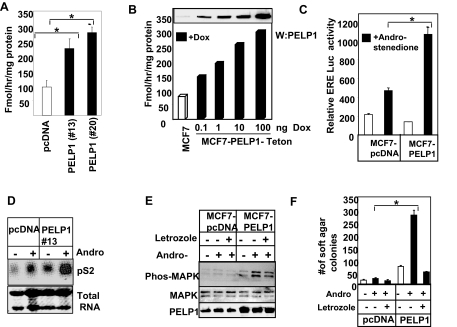
Figure 2.
PELP1 Deregulation Promotes Aromatase Activity and in Situ Estrogen Synthesis
A, Aromatase activity in control MCF7 cells and MCF7-PELP1 clones was measured by tritiated-water release assay. Each experimental condition was measured in triplicate, and aromatase activity was expressed in picomoles per milligram of protein per hour (mean ± sem). B, Tet-inducible PELP1 model cells were treated with increasing doses of doxycycline to induce variable levels of PELP1, and 24 h later, aromatase activity was measured; inset shows induction of PELP1 expression as measured by Western blot analysis. C, MCF7 and MCF7-PELP1 clone cells cultured in DCC medium were transiently transfected with ER reporter gene. After 48 h, the cells were treated with or without the aromatase substrate androstenedione for 12 h, and then reporter gene activity was measured. D, MCF7 and MCF7-PELP1 clones cells were cultured in DCC medium for 2 d and treated with androstenedione for 24 h, and expression of the ER target gene pS2 was measured by Northern blot analysis. E, MCF7 and MCF7-PELP1 clone cells were treated with androstenedione for 24 h and with or without letrozole, and activation of MAPK pathway was measured using Western blot analysis with phosphorylated antibodies. F, MCF7 and MCF7-PELP1 clone cells were plated in soft agar in the presence or absence of androstenedione and with or without letrozole. Colony formations were counted after 21 d. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.001. These experiments were repeated three times; the average of the results is shown in the graph.