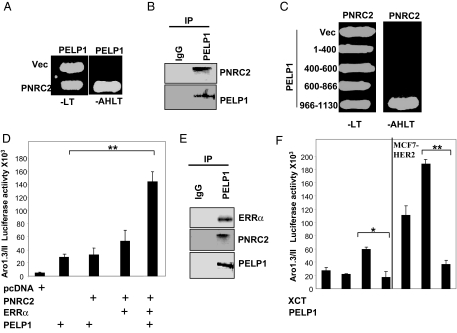
Figure 6.
PELP1 Interacts with PNRC2
A, Yeast cells were transfected with a control Gal4-activation domain vector (Vec) or GAD-PNRC2, along with a Gal4-DNA-binding domain vector or GBD-PELP1. Growth was recorded after 72 h on selection plates lacking leucine and tryptophan (−LT) or adenosine, histidine, leucine, and tryptophan (−AHLT). B, MCF7 cells were treated with 100 ng/ml EGF, and nuclear extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation using a control IgG or a PELP1/MNAR antibody, followed by Western blot analysis using a PNRC2 antibody. C, Gal4 activation domain fusions of PELP1 deletion mutants were used to determine the PNRC2-binding region in PELP1. Positive interactions were selected on agar plates lacking adenine, histidine, leucine, and tryptophan (−AHLT). D, MCF-7 cells were cotransfected with an Aro-1.3/II luciferase reporter, with or without various combinations of PELP1/MNAR, PNRC2, and ERRα. After 48 h, luciferase activity was measured. E, MCF7 cells expressing GFP-PELP1 were treated with 100 ng/ml EGF, and nuclear extracts were immunoprecipitated with the GFP antibody. The presence of ERRα and PNRC2 in the immunoprecipitates was analyzed by Western blot analysis. F, MCF-7 and MCF-7-HER2 cells were cotransfected with Aro-1.3/II luciferase reporter, with or without PELP1/MNAR. After 48 h, cells were treated with XCT790 (5 μm) for 24 h, and luciferase activity was measured. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.001. Data shown are the means ± se from three independent experiments performed in triplicate wells.