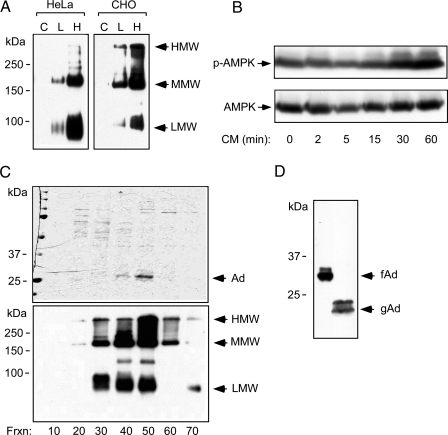
Figure 2.
Purification of Recombinant Adiponectin from Mammalian Cells
A, Adiponectin expression in HeLa or CHO cells. Cells infected with an adenovirus- expressing mouse adiponectin were used to produce recombinant full-length adiponectin (C, L, and H indicate control, low dose, and high virus dose, respectively). Conditioned media (48 h) were subjected to nondenaturing, nonreducing SDS-PAGE. Multimerization of adiponectin was detected by immunoblotting. Arrows indicate the high-, medium (hexamer)-, and low-molecular weight (trimer) multimeric forms. B, Infected cells secrete adiponectin. LβT2 cells were serum starved and treated with conditioned media (CM) for the times indicated. Phosphorylation of AMPK and total AMPK α-subunit were detected by immunoblotting as before. C, Purifcation of recombinant full-length adiponectin from adenovirally infected CHO cells. Recombinant proteins were separated by fast protein liquid chromatography. Protein samples from different fractions, as indicated, were subjected to SDS-PAGE and Coommassie blue staining to determine the purity (top panel). The same samples were subjected to a nonreducing and nondenaturing gel followed by immunoblotting to determine the higher-order structure of adiponectin (bottom panel). Arrows indicate the high (HMW), the medium (MMW), and the low molecular (LMW) form of the recombinant adiponectin. D, Recombinant mouse full-length adiponectin (fAd) and human globular adiponectin (gAd) (a kind gift from Xencor, Inc.) were subjected to SDS-PAGE and detected by immunoblotting.