Figure 3.
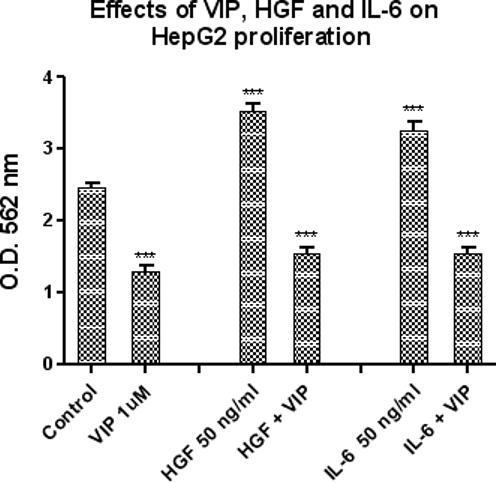
This figure illustrates the effects of VIP (10−6 M), HGF (50ng/ml) and IL-6 (50 ng/ml) on HepG2 cellular proliferation at 72 hours, as measured by MTT assay. IL-6 (50 ng/ml) alone and HGF (50 ng/ml) alone significantly increased HepG2 proliferation by 132% and 143% respectively, as compared to untreated controls (***ρ< 0.001). In contrast, VIP (10−6 M) alone significantly reduced HepG2 proliferation by 47%, again compared to untreated controls (***ρ< 0.001); when VIP was co-administered with Il-6 or HGF, VIP also inhibited the proliferative effects of these cytokines (HGF (50 ng/ml) by 57%, ***ρ< 0.001 and IL-6 (50 ng/ml) by 54%., ***ρ< 0.001). Data is expressed as the mean ± SEM, N = 5.
