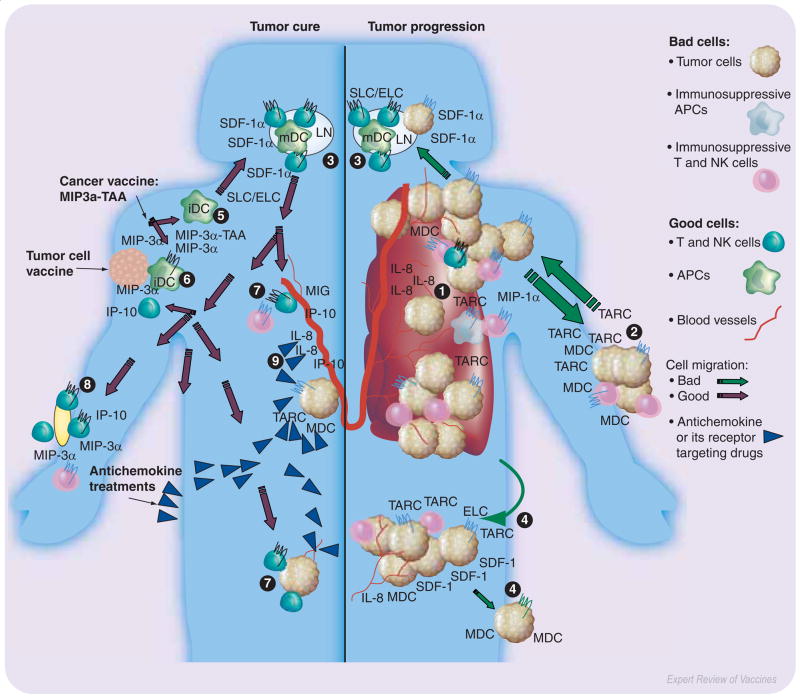
Figure 1. Chemokines are involved in almost every aspect of tumorigenesis and antitumor immunity.
Primary tumors progress producing chemokines (IL-8/CXCL8, MIP-1α/CCL3, TARC/CCL17, MDC/CCL22) that promote neovascularization (1) and escape immunosurveillance via recruitment of immunosuppressive cells, such as T regulatory cells, NK T cells, macrophages and iDC. Tumors metastasize to distant organs, such as skin (2), LN (3), liver (4) and lung, that constitutively produce chemokines (SDF-1/CXCL12, ELC/CCL19 and SLC/CCL21; or TARC/CCL17 and MDC/CCL22). Therefore, to combat the disease and metastatic spread of tumor cells, use of various drugs and specific antibodies that target chemokines or their receptors were proposed, which inhibit neovascularization via expression of angiostatic chemokines (MIG/CXCL9 and IP-10/CXCL10, 9) or depletion of angiogenic chemokines (CXCL8, 9). However, these strategies cannot combat the disease efficiently, particularly relapse, unless they are accompanied with activation of antitumor adaptive immune responses. Immunizations with TAA fused with chemokines (MIP3α-TAA, 5) or with tumor cells modified to express chemokines (MIP-3α/CCL20, IP-10/CXCL10, 6) appear to be potent inducers of antitumor immunity. These vaccines recruit iDCs that take up and present TAAs leading to induction of tumor-specific T-cell responses in secondary lymphoid organs (LN, 3). The activated tumor-specific T cells can efficiently eradicate tumors in the skin (8,2) and other distant sites (7,4). APC: Antigen-presenting cell; DC: Dendritic cell; ELC: EBI1-ligand chemokine; iDC: Immature dendritic cell; IL: Interleukin; IP: Interferon-γ inducible protein; LN: Lymph node; mDC: mature dendritic cellMDC: Monocyte-derived chemokine; MIG: Monokine induged by interferon-γ; MIP: Macrophage inflammatory protein; NK: Natural killer; SDF: Stromal cell-derived factor; SLC: Secondary lymphoid tissue chemokine; TAA: Tumor-associated antigen; TARC: Thymus and activation-regulated chemokine.