Fig. 5.
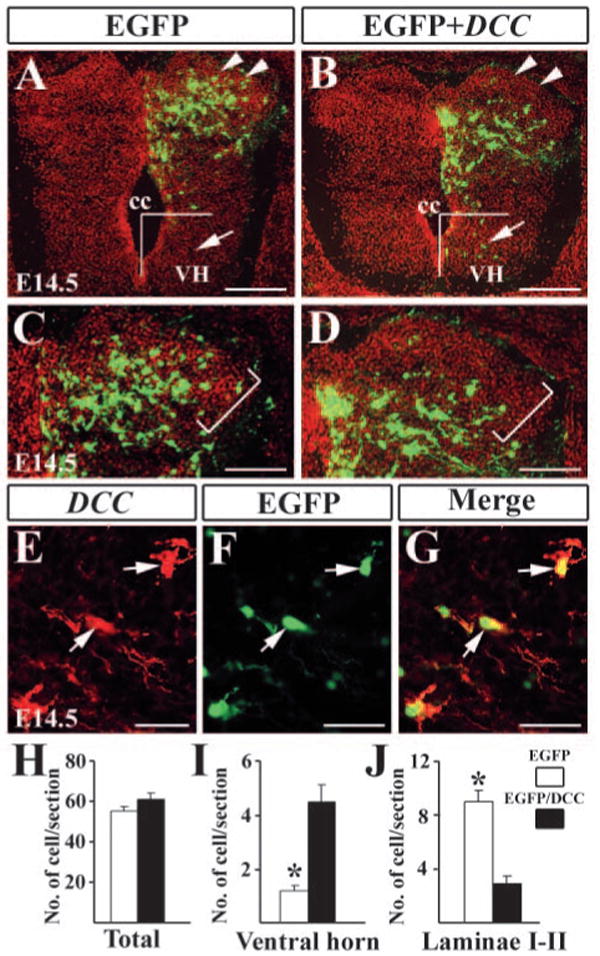
Forced expression of Dcc in the dorsal spinal cord. (A,B) Detection of EGFP in the dorsal spinal cord electroporated with EGFP only (A) and Egfp/Dcc (B) plasmids. There are a few neurons located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord after the electroporation of Egfp/Dcc (arrowheads in B). (C,D) Higher magnification of A,B indicates the superficial dorsal horn. Brackets outline laminae I-II region. In the spinal cord electroporated with EGFP, EGFP+ cells are found in laminae I-II, but few Egfp/Dcc+ cells are present in the corresponding region (D). (E) Dcc immunostaining of Egfp/Dcc electroporated side of the dorsal horn. Arrows indicate Dcc+ neurons in the same region. (F) Arrows indicate EGFP+ neurons. (G) Dcc and Egfp are colocalized in the same cells (arrows). (H-J) Counting of EGFP+ and Egfp/Dcc+ cells in the spinal cord (H), ventral horn (I) and laminae I-II (J). For cell counting in the ventral horn, Egfp/Dcc+ or EGFP+ cells located ventral to the center of the central canal were included, as shown in A,B. For cell counting in laminae I-II, the morphology of the spinal cord is revealed by Hoechst counterstaining (red color in A-D), and labeled cells in laminae I-II, as shown in C,D were counted. Student's t-test was used when making comparisons, *P<0.0001. cc, central canal; VH, ventral horn. Scale bars: 200 μm in A,B; 100 μm in C,D; 25 μm in E-G.
