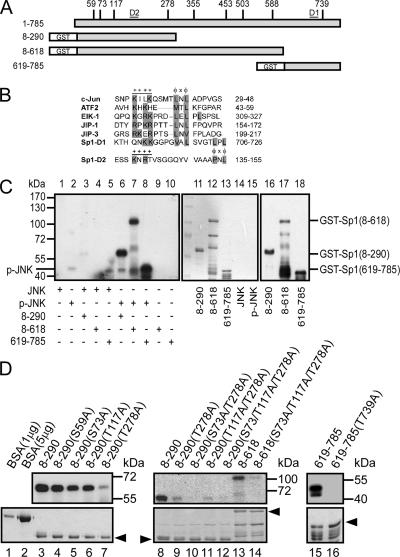
Figure 6.
JNK phosphorylated the Thr278/739 sites of Sp1. (A) The potential JNK-phosphorylated Thr/Ser sites of Sp1 are indicated (S59, S73, T117, T278, T355, T453, T503, S588, and T739), and different GST-Sp1 deletion constructs are also indicated. (B) Known D-sites in JNK-binding proteins aligned with the putative D-sites in Sp1. D1 and D2 are located in residues 706-726 and residues 135-155, and they are marked in A. Consensus basic (+) and hydrophobic (φ) residues are shown in a gray background. (C) The different GST-Sp1 fragments (amino acids [aa] 8-290, aa 8-618, and aa 619-785) were combined with [γ-32P]ATP and activated JNK for an in vitro kinase assay (lanes 6–8). The expressions of these fragments were detected using Coomassie Blue (lanes 11–15) or immunoblotted using anti-Sp1 antibodies (lanes 16–18). (D) The potential JNK-phosphorylated serine/threonine sites were mutated to alanine as indicated. These mutated GST-Sp1 proteins were expressed in E. coli and purified. The yields of these mutants were detected using Coomassie Blue staining (bottom). Products were analyzed as described in C. Bovine serum albumin (BSA) was used to compare the concentration of proteins in Coomassie Blue staining.