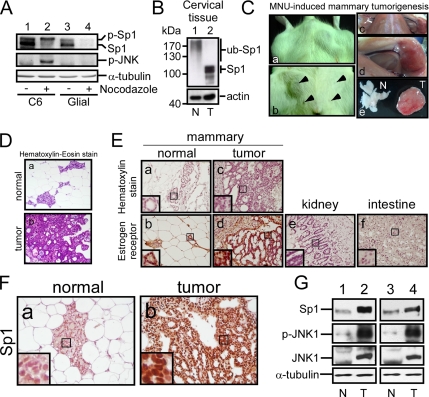
Figure 8.
Sp1 accumulation and JNK activation in glioma cells and MNU-induced tumor. (A) Rat glioma C6 cell line (lanes 1 and 2) and primary glial cells from postnatal day 0 to day 1 rat pups (lanes 3 and 4) were treated with nocodazole for 24 h, and then they were divided into interphase and mitotic cells. These cellular extracts were probed using anti-Sp1 and p-JNK antibodies. The α-tubulin was used as an equal loading control. (B) The normal cervical tissue (N) and cervical cancer tissue (T) were subjected to immunoblot analysis by using antibodies against Sp1. Actin was used as an equal loading control (C) Rats intraperitoneal injected with 50 mg/kg MNU were killed after 8 wk, and the normal and tumor tissues were then harvested. The arrow indicated the nipple position. (D) H&E staining was performed to determine the tissue and tumor type. (E) Estrogen receptor recognized by its antibodies inside the tissue was considered as a mammalian cancer marker. The intestine and kidney tissues were used as the negative control. (F) Sp1 level was determined in the normal and tumor mammalian tissues by immunohistochemistry by using anti-Sp1 antibodies. (G) The level of Sp1, JNK1, and p-JNK1 in normal and tumor tissues was studied by immunoblot with anti-Sp1, anti-JNK1, and anti-phospho-JNK antibodies, respectively.