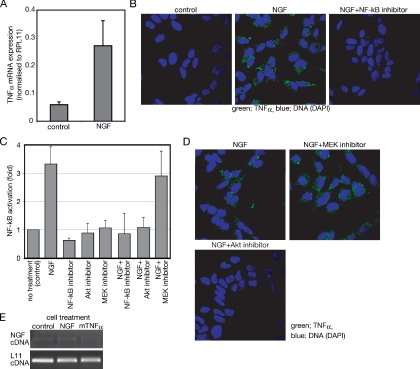
Figure 1.
NGF induces TNF-α expression in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. (A) Semiquantitative analysis of TNF-α mRNA prepared from cells incubated with or without (control) NGF for 24 h. Expression level of TNF-α is shown relative to RPL11 expression. The data represent the mean of three experiments. Error bars indicate SE; p < 0.001. (B) Effect of the NF-κB inhibitor on the TNF-α expression induced by NGF. Cells cultured on chambered glass slides were treated for 24 h with or without (control) NGF in the presence or absence of the NF-κB inhibitors. After fixation, TNF-α was detected with anti-TNF-α antibody and visualized by FITC-labeled secondary antibody. (C) Measurement of NF-κB activity after NGF treatment. After transfection of pNFkB SEAP vector, SH-SY5Y cells were treated as described in Materials and Methods section. Activation of NF-κB was measured as enzymatic activity of SEAP in each culture media. The NF-κB activities are shown relative to the NF-κB activity of untreated samples. The data represent the mean of three experiments. Error bars indicate SE. (D) Effect of the inhibitors on the TNF-α expression induced by NGF. Cells were treated as described in B. Either the Akt inhibitor or the MEK inhibitor was used instead of the NF-κB inhibitor. (E) PCR of NGF and L11 ribosomal protein cDNA prepared from cells treated with the indicated reagents for 24 h.