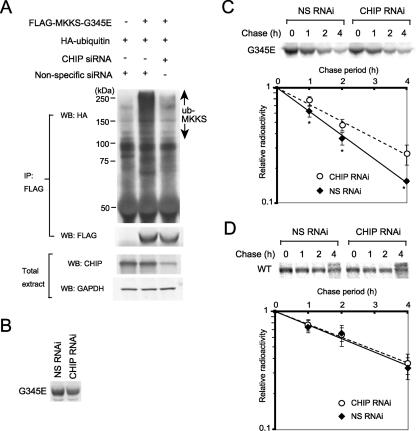
Figure 7.
Polyubiquitination and degradation of the G345E mutant are inhibited by RNAi-mediated knockdown of CHIP. (A) Strong inhibition of MKKS-G345E polyubiquitination by CHIP knockdown. After cotransfection with FLAG-tagged G345E and HA-tagged ubiquitin, cells were treated with CHIP siRNA or nonspecific siRNA as a control. FLAG-G345E was immunoprecipitated with the anti-FLAG antibody and analyzed by Western blotting by using antibodies against HA or FLAG. Expression levels of CHIP were analyzed by Western blotting of total cell extracts. (B) Decreased synthesis of MKKS-G345E by CHIP RNAi treatment. Transiently expressed FLAG-tagged G345E was pulse labeled with [35S]Met for 30 min. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with the anti-FLAG antibody and analyzed by SDS-PAGE. (C and D) Transiently expressed FLAG-tagged G345 mutant (C) and wild-type MKKS (D) were pulse labeled with [35S]Met for 30 min and chased for 1, 2, and 4 h in the presence of CHIP siRNA or nonspecific siRNA as a control. The radiolabeled FLAG-MKKS was immunoprecipitated and analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Radioactivity of FLAG-tagged MKKS bands in pulse-chase experiments was determined and normalized against the value of chase at 0 h (n = 5 in C and n = 4 in D). Asterisks indicate significance of difference (p < 0.02).