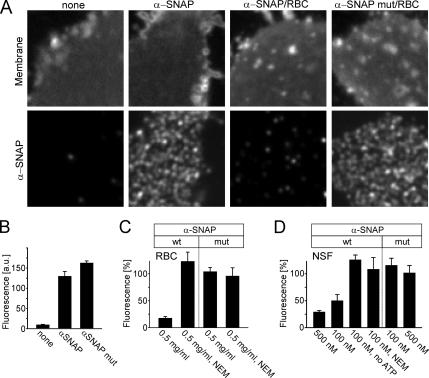
Figure 3.
Membrane sheets contain NSF-sensitive binding sites for α-SNAP. (A) Membrane sheets incubated for 5 min with recombinant α-SNAP or α-SNAPL294A were briefly washed, fixed, and immunostained for α-SNAP (bottom). Top, membrane sheets visualized using TMA-DPH (also see Figure 1A). Where indicated, RBC was included in the incubation. (B) Quantification of immunofluorescence intensity in the absence or presence of recombinant α-SNAP or α-SNAPL294A. For better comparison, in the following experiments (C and D; also see Figure 5) values were normalized to the corresponding immunoreactivity stainings in B. (C and D) Binding of α-SNAP (wt) but not of α-SNAPL294A (mut) is prevented by the inclusion of either RBC (C) or purified NSF (D). Addition of NEM (1 mM) or omission of ATP, both known to inactivate NSF, blocked the interference with α-SNAP binding by both rat brain cytosol and purified NSF. The concentrations of RBC (milligrams of protein per milliliter) and recombinant NSF (nanomolar) is given at the bottom of the columns. Values are given as mean ± SEM (n = 3–14 independent experiments, with 35–169 individual membrane sheets analyzed for each experiment).