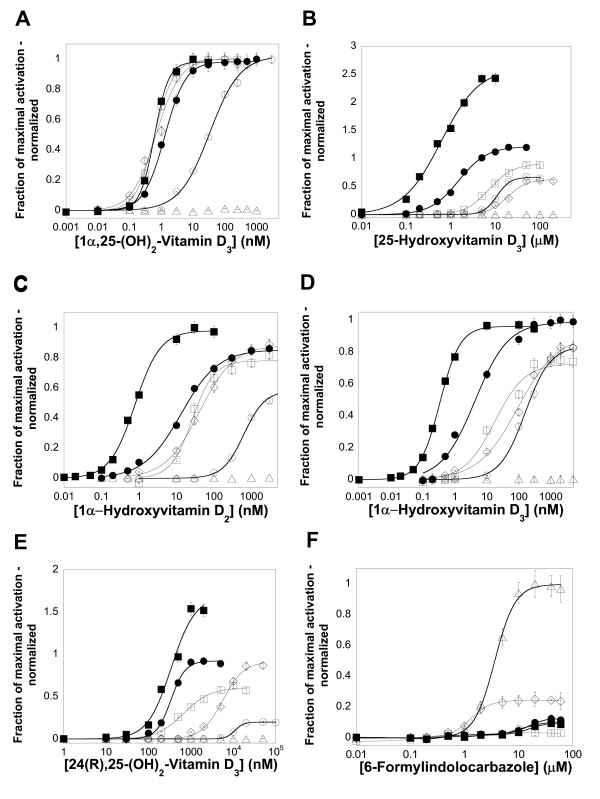
Figure 2.
Concentration-response curves for activation of VDRs by vitamin D derivatives and 6-formylindolo [3,2-b]carbazole. The ordinate represents activation of VDR, relative to vehicle control, and normalized to the maximal activator (0.5 μM calcitriol for mouse and sea lamprey VDRs; 1 μM calcitriol for human, frog, and zebrafish VDRs; 20 μM 6-formylindolo [3,2-b]carbazole for Ciona intestinalis VDR/PXR). (A)-(E) Human (●), mouse (■), frog (○), zebrafish (□), and sea lamprey (◇) VDRs are all activated by vitamin D derivatives while the Ciona intestinalis VDR/PXR (Δ) is insensitive to all vitamin D compounds. (F) The planar molecule 6-formylindolo [3,2-b]carbazole activates most vertebrate VDRs (i.e., all except zebrafish VDR) weakly and the Ciona VDR/PXR at low micromolar concentrations.