Figure 1.
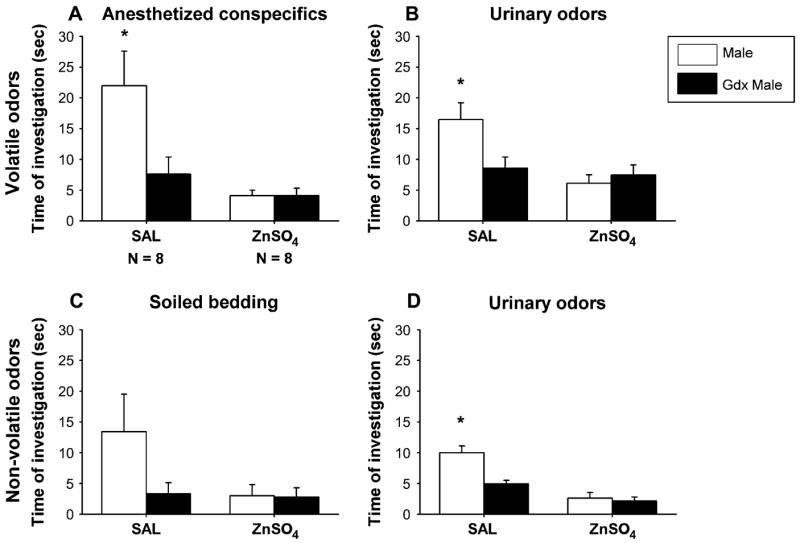
The mean (±SEM) amount of time that female mice spent investigating volatile (A, B) and nonvolatile (C, D) odor stimuli derived from intact male versus castrated (gdx) male in a Y-maze. Females had received either intranasal irrigation with zinc sulfate to destroy the MOE (ZnSO4) or saline to serve as control (SAL), prior to behavioral testing. *P < 0.05, post hoc comparisons between time spent investigating intact male versus castrated male odor by SAL females.
