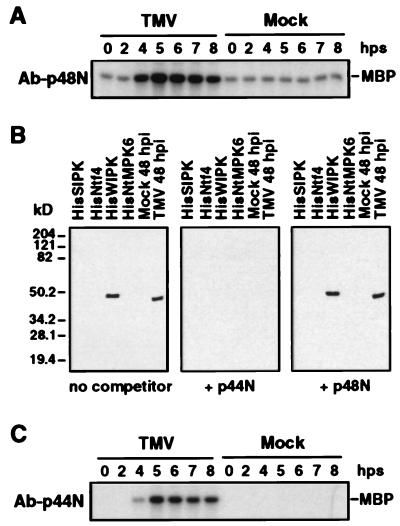
Figure 2.
Immune-complex kinase assays using sequence-specific antibodies against SIPK and WIPK. (A) Immune-complex kinase assay of TMV-activated kinase using SIPK-specific antibody, Ab-p48N. Protein extracts (50 μg) from TMV- or mock-inoculated leaf tissue were reacted with Ab-p48N (2.5 μg). The resultant antigen–antibody complex was precipitated with protein A-agarose beads and washed extensively before addition to a kinase assay mixture with [γ-32P]ATP and MBP as substrates. The reaction mixture, including the phosphorylated MBP, was then fractionated by SDS/PAGE. (B) An antibody raised against a peptide (p44N) corresponding to the unique N terminus of WIPK, Ab-p44N, specifically recognized the WIPK protein. Two nanograms each of recombinant HisSIPK, HisNtf4, HisWIPK, and HisNtMPK6 or 20 μg of protein extracts from 48-hr mock- or TMV-inoculated tobacco leaves (maintained throughout infection at 22°C) were subjected to immunoblot analysis with Ab-p44N in the absence or presence of 0.2 μg/ml competitor peptides p44N or p48N. (C) Immune-complex kinase assay of TMV-activated kinase using WIPK-specific antibody, Ab-p44N. Protein extracts (50 μg) from TMV- or mock-inoculated leaves were immunoprecipitated with Ab-p44N (2.5 μg), and the kinase activity of the immune-complex was determined as above. Times in A and C are given in hps from 32°C to 22°C.