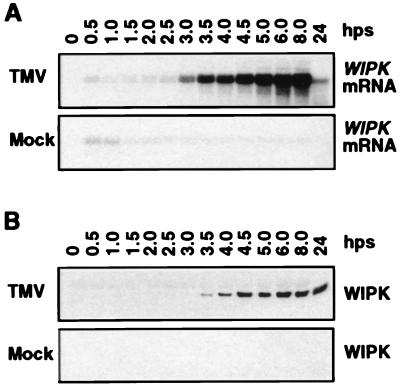
Figure 3.
Activation of WIPK gene expression by TMV in tobacco plants [cv. Xanthi nc (NN)] after temperature shift. (A) Increase in steady-state levels of WIPK mRNA in TMV-infected plants. Duplicates of leaf discs used in Fig. 1 were extracted for total RNA, thus facilitating direct comparison of the induction kinetics of mRNA and enzymatic activity. Twenty micrograms of total RNA per lane was separated on 1.2% formaldehyde/agarose gels and transferred to Zeta-probe membranes. Blots were hybridized with random primer-labeled inserts consisting of either a full-length cDNA of WIPK (data shown) or its 3′ untranslated region (data not shown). Equal loading of RNA was confirmed by ethidium bromide staining of the rRNA (data not shown). (B) Increase of WIPK protein in TMV-infected tobacco after temperature shift. Samples containing 20 μg of protein from the leaf extracts used for Fig. 1A were separated on 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gels. After blotting to nitrocellulose, the WIPK protein was detected with Ab-p44N.