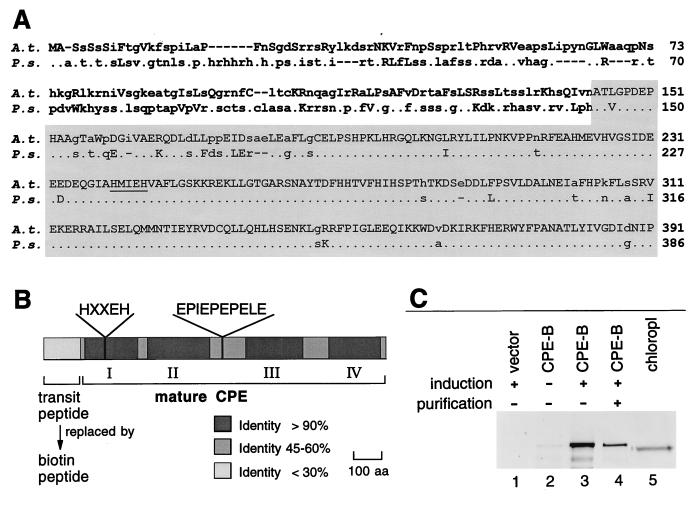
Figure 1.
Structure of CPE and expression of CPE-B fusion protein. (A) Alignment of N-terminal amino acid sequences of A. thaliana (A.t.) and P. sativum (P.s.) preCPE. Lowercase letters indicate different amino acids. Uppercase letters indicate amino acids with a homology index ≥0.8 (28). Dots represent identical amino acids. Sequence of mature CPE predicted from the alignment is indicated by shading. The zinc binding motif is underlined. (B) Schematic map defined by amino acid comparison of pea and Arabidopsis CPE. The highly conserved regions I to IV, the zinc-binding motif of conserved region I, and a putative flexible linker are indicated. To express active CPE, the predicted transit peptide was replaced by a biotin-containing peptide (CPE-B). (C) Western blot analysis of CPE-B expression in E. coli using the anti-145/143-kDa antibody was carried out as described (7). Soluble cell extracts of induced cells carrying pBEX5BA (lane 1), and of uninduced and induced cells carrying pCPE-B (lanes 2 and 3, respectively). CPE-B was partially purified with avidin-resin demonstrating biotinylation of the fusion protein (lane 4). Soluble chloroplast extract containing CPE (lane 5) was prepared as described (3).