Figure 5. BCR mediated signaling and B cell development in competitively reconstituted chimeras.
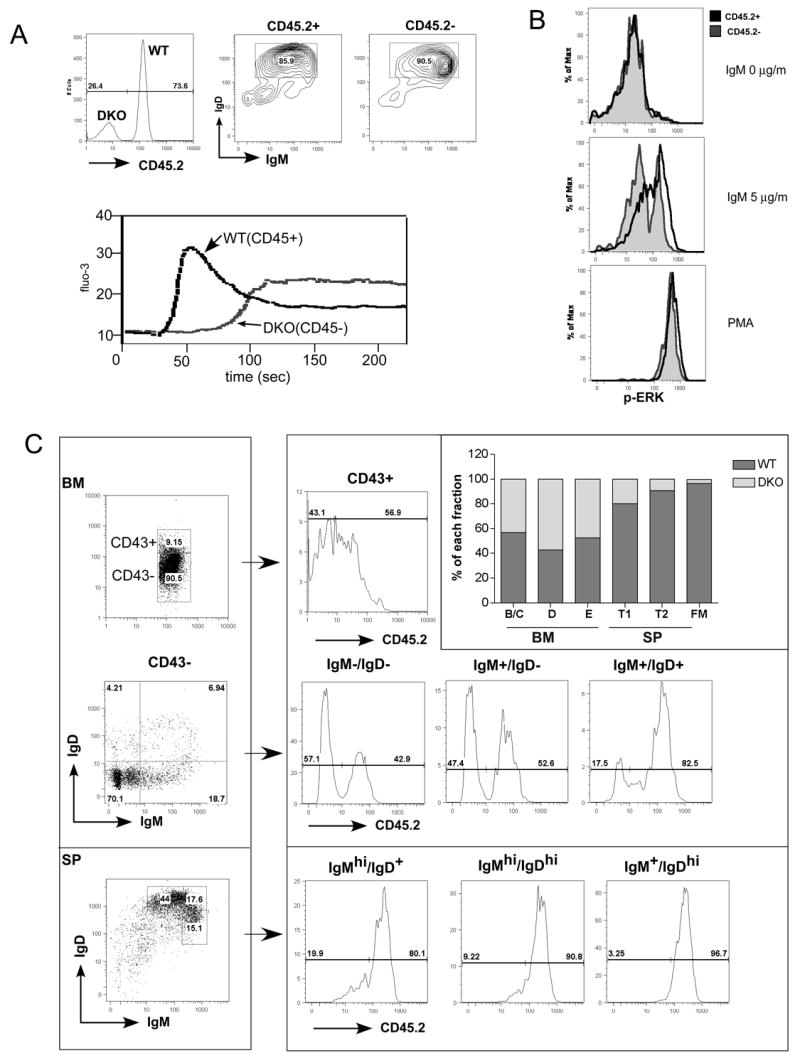
(A) Cell autonomous defect in intracellular free Ca2+ increase. Lethally irradiated recipient mice were reconstituted with BM from CD45/CD148 DKO and WT control mice. The donor origins of reconstituted B cells were identified using CD45.2 as a congenic marker: WT B cells were CD45.2+ and DKO B cells were CD45.2-. Lymph node B cells were stained with CD45.2 (upper left) and IgM /IgD (upper right) antibodies. The intracellular free Ca2+ levels were monitored before and after addition of IgM F(ab')2 (5μg/ml). (B) Cell autonomous defect in activation of ERK. Purified B cells as in (A) were stimulated with IgM F(ab')2 (5μg/ml) or PMA for 2.5 minutes, fixed, permeabilized and then stained with phospho-ERK along with other surface makers. Follicular mature B cells (IgM+IgD+CD23+) were separated based on the origin of the donors (same as in (A)). Phospho-ERK levels of CD45.2+ (WT origin) and CD45.2- (DKO origin) upon indicated stimulation were overlaid in histograms. (C) B cell development in competitively reconstituted chimera. Cells from BM and spleen were isolated and stained with antibodies as indicated. For BM, CD19+ B cells were gated to separate CD43+, and CD43-. The CD43- cells were further subdivided based on expression of IgM and IgD. For the spleen, CD19+ B cells were separated based on IgM and IgD expression. The donor origin of each subset was then identified by CD45.2 staining. Percentages of WT and DKO B cells of each sunset were presented in the overlaid bar graph. Results in (C) are representive of 4 independent experiments.
