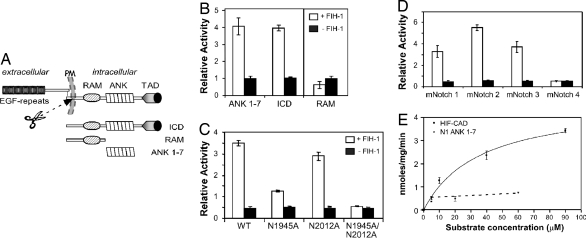
Fig. 1.
Hydroxylation of Notch ICD at 2 asparagine residues by FIH-1. (A) Schematic diagram showing key features of Notch. (B) Notch 1 ICD, ANK 1–7, and RAM proteins were analyzed in a 14CO2 capture assay. Data are mean relative activity ± range (n = 2) and are representative of >3 independent experiments. (C) Purified wild-type (WT) or Asn mutant ANK 1–7 proteins or (D) mNotch 1–4 ANK 1–7 proteins were compared for their abilities to promote FIH-1-mediated 2-oxoglutarate turnover. Data are presented as mean ± range (n = 2) and are representative of three independent experiments. (E) Kinetic CO2 capture assay with varying HIF-CAD or mNotch1 substrate concentrations, with data fitted to a hyperbolic curve using PRISM software. The HIF-CAD apparent Km is 36 μM, and the apparent Vmax is 4.7 nmol/mg per min, whereas Notch hydroxylation rate is near-maximal (≈0.7 nmol/mg per min), and the apparent Km cannot be determined accurately (<4 μM). Data are mean nmol/mg per min ± range (n = 2), representative of >3 independent experiments.