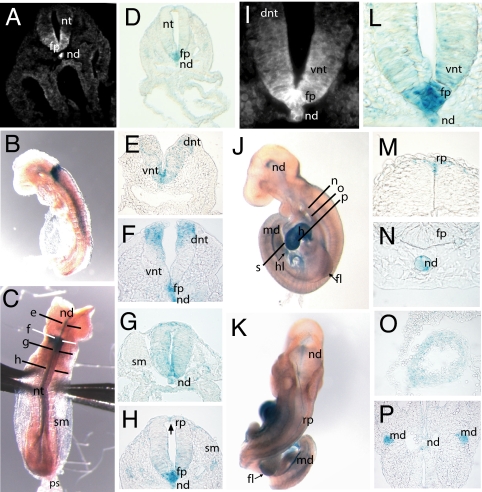
Fig. 2.
Vangl1 expression during neurulation. (A and I) Detection of Vangl1 protein in E8.5 WT embryos by using a rabbit anti-Vangl1 polyclonal antiserum (magnification, ×200 and ×630). (B and C) Whole-mount X-gal staining on E8.5 Vangl1gt/gt embryos showing lateral and dorsal views, respectively. The section planes used for E–H are shown in C. (D and L) Section of Vangl1gt/gt E8.5 embryo stained with X-gal showing a pattern of Vangl1 expression in notochord and floor plate very similar to that detected with anti-Vangl1 antiserum (magnification, ×200 and ×630) (E–H). Transverse sections and X-gal staining of neural tube (E8.5) arranged in rostral–caudal progression (magnification, ×400). (J and K) Whole-mount X-gal staining of Vangl1gt/gt E9.5 embryos; the section planes used for M–P are shown in K. (M–P) X-Gal staining of E9.5 Vangl1gt/gt embryos; transverse sections (magnification, ×400). (O and P) X-Gal staining of myocardial cells of heart (O) and epithelium of mesonephric duct (P). fp, floor plate; dnt, dorsal neural tube; h, heart; hl, hindlimb; md, mesonephric duct; nd, notochord; nt, neural tube; ps, primitive streak; rp, roof plate; sm, somites; vnt, ventral neural tube.