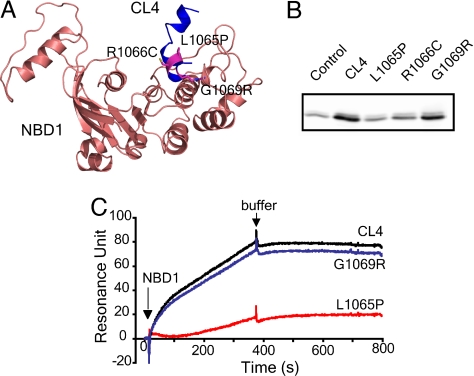
Fig. 2.
CL4 peptide binding to NBD1. (A) Location of disease-associated mutations (L1065P, R1066C, and G1069R) at the NBD1/CL4 interface. (B) Disease-causing mutations in CL4 abolish or diminish the CL4 and NBD1 interaction. Biotinylated CL4 or its mutant peptides immobilized on NeutrAvidin beads were incubated with purified recombinant human NBD1 (see SI Text). Bound proteins were eluted with sample buffer and detected by Western blotting with CFTR antibody 660. NeutrAvidin beads without bound peptide were used as control. (C) CL4 binds to NBD1 as detected with surface plasmon resonance. Biotinylated peptides were immobilized on a BIAcore streptavidin sensor chip to 200 resonance units. NBD1 was injected, and the binding was detected by surface plasmon resonance and BIAcore 2000. The binding of NBD1 to the chip without peptide was subtracted from NBD1 binding to the peptides.