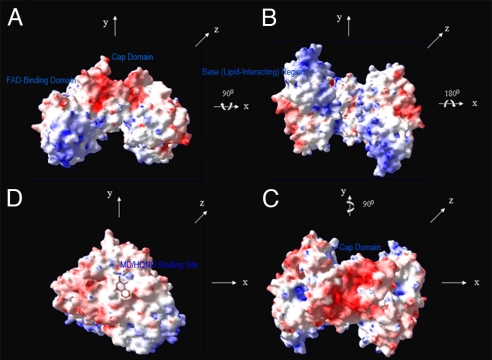
Fig. 3.
Electrostatic potential maps. Electrostatic potential surfaces in blue for positive (+8kT), white for hydrophobic, and red for negative (−kT). High positive potentials at found at the base region, defining surfaces likely to be involved in interacting with the negatively charged phospholipid head groups of the membrane. (A) With the cap domain at top, distinct segregation of potentials with clustering of negative potentials at one end (cap) and positive potentials at the opposite end (base of the FAD-domain). (B) Shown 90° from A, looking up at the base, regions of extensive hydrophobic patches are found, in white. (C) Shown 180° from B, view looking down the red cap domain, with the hydrophobic surfaces located at periphery of GlpD. (D) Shown 90° from C, a hydrophobic plateau is found with a MD bound and may be the putative UQ docking site.