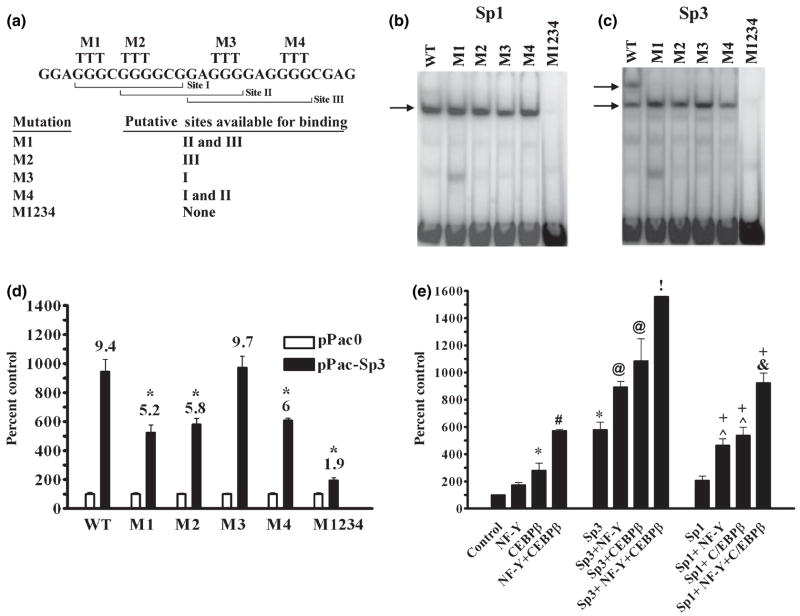
Fig. 5.
Mutation of the GC-box supports a triad model in which Sp1 and Sp3 interact with C/EBPβ and NF-Y to activate transcription. (a) Mutagenesis was performed based upon the triad model of the GC-box. In each case a GGG within a site was replaced with a TTT and is labeled above. Mutation M1 within Site I forces Sp-protein binding to Sites II or III while mutation M2 within Sites I and II forces binding to Site III. Similarly, mutation M3 within Sites II and III forces binding to Site I while mutation M4 within Site III forces binding to Sites I or II. Mutation M1234 in Sites I, II, and III eliminates Sp-protein binding completely. (b) EMSA using 1 μg of nuclear protein from SL2 cells transiently transfected to express Sp1 demonstrates that mutations M1, M2, M3 and M4 do not affect binding to the GC-box whereas mutation M1234 completely eliminates Sp1 binding. (c) EMSA using 1 μg of nuclear protein from SL2 cells transiently transfected to express Sp3 shows that mutations M1, M2, M3, and M4 prevent formation of the large Sp3 complex without affecting formation of the smaller complex whereas mutation M1234 completely eliminates Sp3 binding. (d) Luciferase assays of SL2 cells transiently co-transfected with 780 ng of wild-type (WT) p0.27GCH1-GL3 or the reporter constructs containing GC-box mutations shown in Fig. 5a, M1, M2, M3, M4 or M1234 along with 20 ng of pPac-0 or 20 ng of pPac-Sp3. Data were analyzed by ANOVA and post hoc Bonferroni tests (*p < 0.05 vs. WT pPac-Sp3). (e) Luciferase assays of SL2 cells transiently transfected with the 600 ng of wild-type p0.27-GCH1-GL3 reporter along with various combinations of 50 ng pPac-NF-YA, B and C, 50 ng pPac-C/EBPβ, 20 ng pPac-Sp3, 20 ng of pPac-Sp1 and varying amounts of pPac-0. Data were analyzed by ANOVA and post-hoc Bonferroni tests (*p < 0.05 vs. pPac-0; #p < 0.05 vs. pPac-C/EBPβ; @p < 0.05 vs. pPac-Sp3; !p < 0.05 vs. pPac-Sp3 + pPac-C/EBPβ; + p < 0.05 vs. pPac-Sp3 + pPac-NFY or pPac-C/EBPβ; &p < 0.05 vs. pPac-Sp3 + pPac-NF-Y + pPac-C/EBPβ).