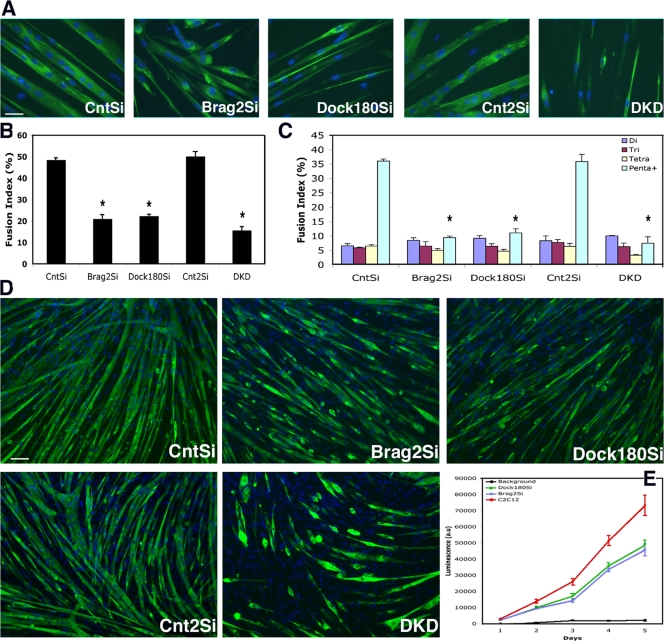
Figure 2.
Brag2- and Dock180-deficient cells have similar fusion index but disparate myotube morphologies. (A) Immunofluorescence images from each cell line, after d 6 in DM. Cells were labeled with primary antibody to MHC and secondary Alexa 488 (green) and Hoechst 33258 (blue). Bar, 50 μm. (B) Total fusion index analysis representing the number of nuclei in multinucleated myotubes divided by total number of nuclei in a field, with a myotube defined by at least three nuclei. A minimum of 4,000 nuclei were counted from random fields of each line at d 6 in DM. P value was determined with a t test, in which CntSi served as control for Brag2Si and Dock180Si cells and Cnt2Si served as control for DKD (*, P < 0.00001). (C) Fusion index analysis indicating the formation of di-, tri-, tetra-, or penta+ multinucleated myotubes after d 6 in DM. All error bars indicate the mean ± SE of at least four independent determinations (*, P < 0.00001). (D) Representative immunofluorescence images of d 6 DM fields used in the fusion index analysis. Bar, 200 μm. (E) β-gal complementation assay of fusion of Brag2Si, Dock180Si, and C2C12 control cells containing equal populations of α- and ω-fragments over the course of 5 d in DM. Background luminescence determined by C2C12 control cells containing α- and ω-fragments of β-gal seeded under proliferation conditions. (n = 3).