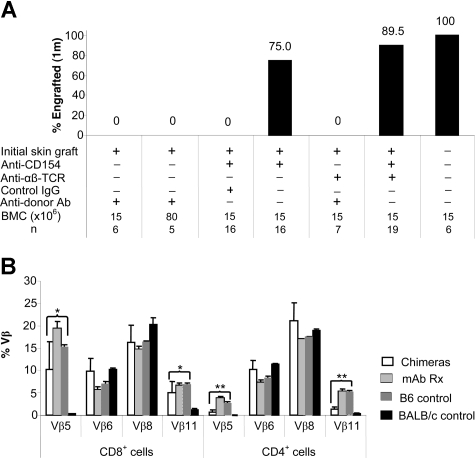
Figure 5.
Characterization of allogeneic BM engraftment. (A) BMT was performed 5 to 7 weeks after the treatment with anti-CD154 mAb and/or anti-αβ TCR mAb at the time of initial skin grafting. Naive, sensitized, and control IgG–treated B6 mice served as controls. Recipients were conditioned with 950 cGy TBI and received transplants of 15 × 106 or 80 × 106 untreated BALB/c donor BMCs via lateral tail vein injection 4 to 6 hours after irradiation. Animals were analyzed for engraftment using flow cytometric analysis 4 weeks after BMT by determining the relative percentages of donor-derived PBLs. The results are the summarized from 3 experiments. (B) Relative TCR-Vβ expression. Expression of Vβ5.1/2, Vβ6, Vβ8.1/2, and Vβ11 on PBLs from unmanipulated hosts (B6 [▨]; n = 4), unmanipulated donors (BALB/c [■]; n = 4), mixed chimeras (chimeras [□]; n = 9), or recipients treated with both anti-CD154 and anti-αβ TCR that had skin graft acceptance (mAb Rx ▩; n = 5), was measured by FACS analysis. The chimerism ranged from 65.6% to 93.6% donor. Relative expression in chimeras represents the percentage of Vβ+ cells within the CD8+ or CD4+ T-cell subsets of the host lymphocytes in peripheral blood. Samples from mixed chimeras were stained 2 months after reconstitution. The samples from skin graft–tolerant mice treated with anti-αβ TCR plus anti-CD154 mAb were tested 5 to 7 weeks after skin grafting. Data from 3 experiments are depicted as means plus or minus SD. TCR-Vβ expression in either the chimeric group or the mAb-treated tolerant group was compared with that in B6 mice using the 2-tailed t test (2-sample, assuming unequal variances). Significant P values are indicated above the respective data bars (*P = .02; **P < .001).