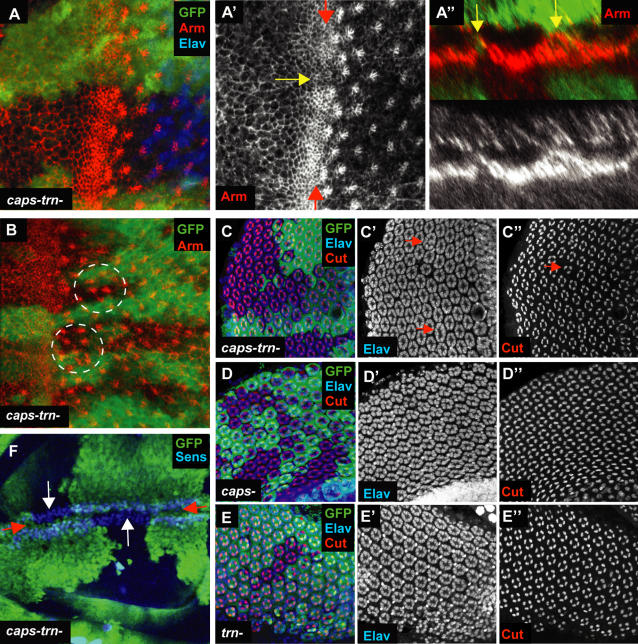
Figure 5. caps trn double null clones.
(A) capsDel1 trn28.4 double null clones in the 3rd instar eye disc. Mutant tissue is marked by lack of GFP (green). Anti-Elav marks all photoreceptors. Anti-Armadillo (Arm) marks the apical surface of cells and is accumulated at a high level in the apically constricted cells of the furrow. At the border between wild type and capsDel1 trn28.4 tissue, there is a reduction in Arm accumulation in the cells of the furrow and the apical surface of cells is expanded (yellow arrow A'). (A”) A Z-section along the furrow (between the two red arrows in A'). At the clone boundaries, cells are taller in the apical-basal direction, producing ‘bumps’ in the furrow (two yellow arrows). (B) A capsDel1trn28.4 clone (marked by lack of GFP, green) where ommatidia near the clone boundaries are mis-positioned (circled in white). (C) capsDel1trn28.4 clones in pupal retinae (marked by lack of GFP, green). Elav is used to mark the photoreceptors and Cut is used to mark cone cells (four per ommatidium) [27]. At mutant-wild type borders neighbouring ommatidia sometimes fuse with each other (red arrows in C'). Correct cone cell numbers are also sometimes disrupted (red arrow in C”). (D) capspB1 clones in pupal retinae (marked by lack of GFP, green). No defects in mutant tissue or clone boundaries can be seen. (E) trn28.4 clones in pupal retinae (marked by lack of GFP, green). Again, the retinae are phenotypically wild type. (F) capsDel1trn28.4 clones in the wing (marked by lack of GFP, green) do not visibly affect the DV boundary (between the two red arrows), as marked by anti-Senseless (Sens). Clones do not cross the DV boundary (white arrows).