Fig. 2.
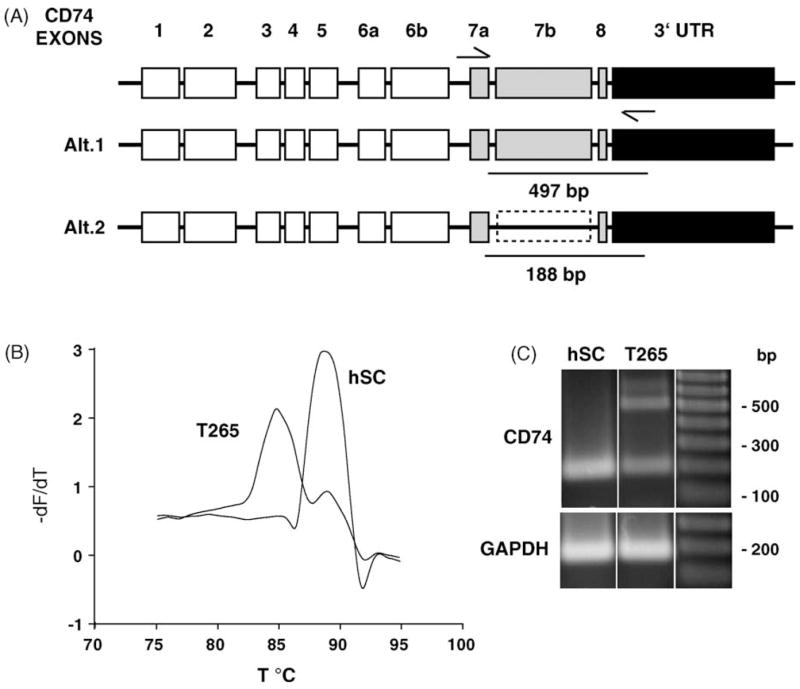
CD74 is differentially regulated in hSC and T265. (A) CD74, a MHC class II chaperone, exon structure and potential alternative splice forms. CD74 spans 11 kb on chromosome 5 and is comprised of 8 exons. Exon 7b may arise from alternate usage of splice donor and acceptor sites that utilize intron sequence. (B) Melting curve analysis of LightCycler PCR products demonstrates an additional product present in T265 cell PCR sample. Melting curve analysis was performed following LightCycler PCR. Plotted is the dF/dT as a function of temperature (°C) to define the melting point of amplified PCR products. The peaks correspond to different products, at 85 and 89 °C. There is an additional product that is present in the T265 cells, evident by the presence of the second peak at 85 °C. (C) RT-PCR of hSC and T265 cells demonstrate the presence of an alternatively spliced transcript. Primers corresponding to exon 7a and within the 3′UTR, amplify a single product of 188 bp in hSC, and an additional 497 bp product in the cancer cell line. This larger product may arise from utilization of intronic sequence between exons 7a and 8.
