Figure 1. .
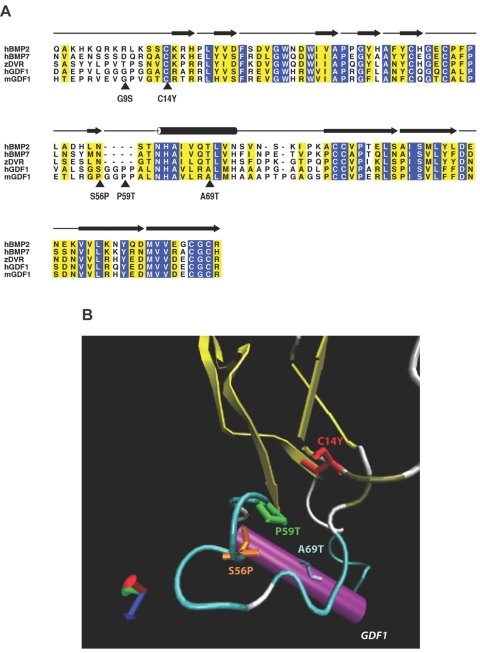
Structural analysis of GDF1 mutations. A, Alignment of human GDF1 (hGDF1) and structurally related members of the TGF-β family, including human BMP2 (hBMP2), human BMP7 (hBMP7), zebrafish DVR (zDVR), and murine Gdf1 (mGDF1). Amino acid residues showing absolute identity are shown with white letters against a blue background; those positions with conservative substitutions are shown against a yellow background. The positions of the five mutations considered in this study are indicated by arrowheads. The amino acid numbering is based on that of the mature processed ligand. The β-sheet elements of the winglike finger projections F1 and F2 are indicated by blackened arrows above the alignment, whereas the α-helical core is denoted by the cylinder above the alignment. B, Ribbon diagram of human GDF1, showing the position of the mutations clustered in the knuckle region of the monomer. (Note that the G9S variant lies within the poorly conserved N-terminal region of the protein where the crystal structure is unknown, precluding accurate modeling of this mutation.)