Figure 5.
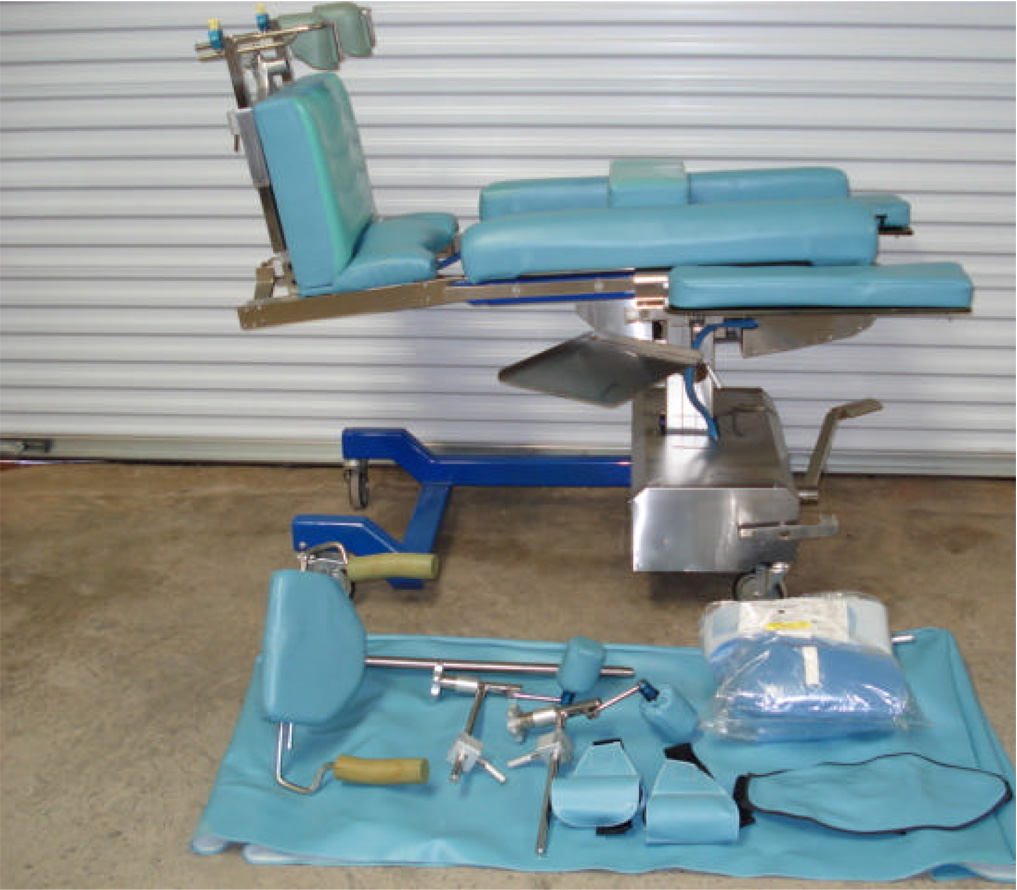
(A) Prone positioning and the main frames used for spine surgery. Wilson frame. Positioning on the Wilson frame: abdomen is partially compressed, pelvis is partially supported, legs are positioned below the trunk, head is positioned on the pillow (Adapted with permission from Youmans Neurological Surgery, Fifth Edition, pp 559, 601(3)); (B), (C) – Wilson frame.
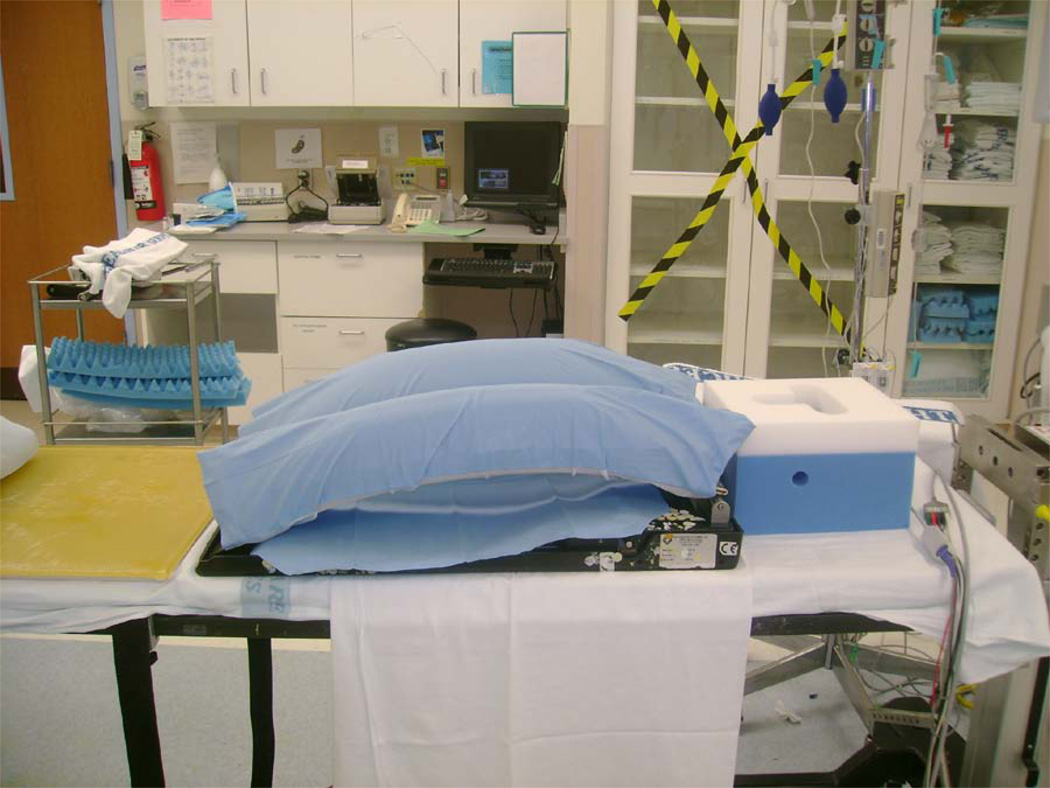
(D). Andrews frame. Positioning on the Andrews frame: abdomen hangs free, pelvis is partially supported, legs are positioned below the heart, head is positioned on the foam pillow, or headrest; (E) – Andrews frame (OSI ANDREWS SST 3000 model 5820 Spine Surgery Table, Ideal Medical, Monroe, GA, www. idealmedicalequipment.com)
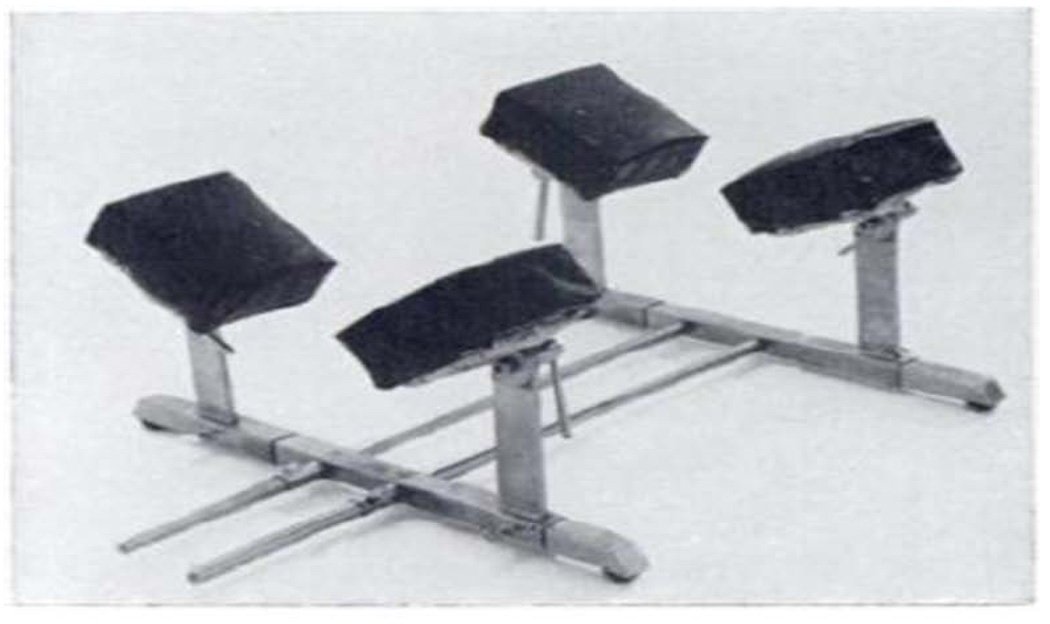
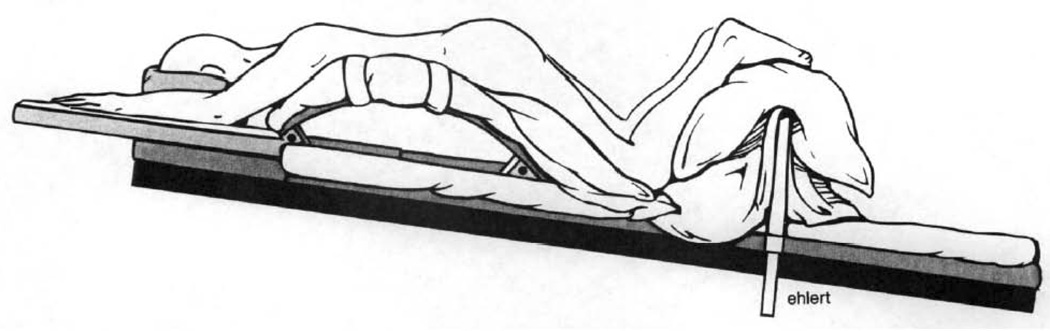
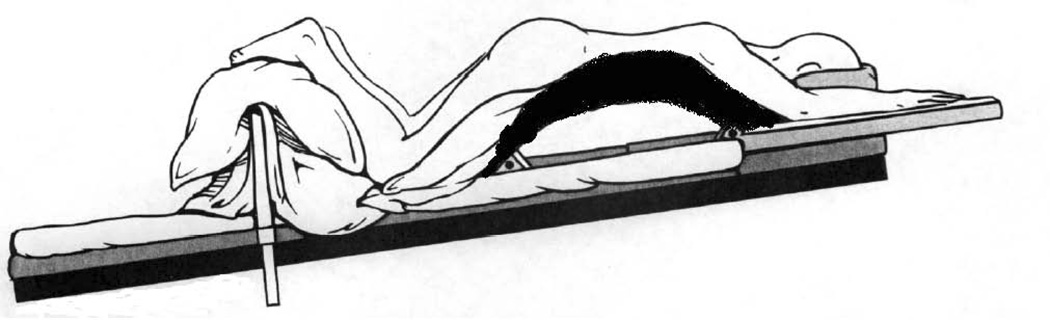
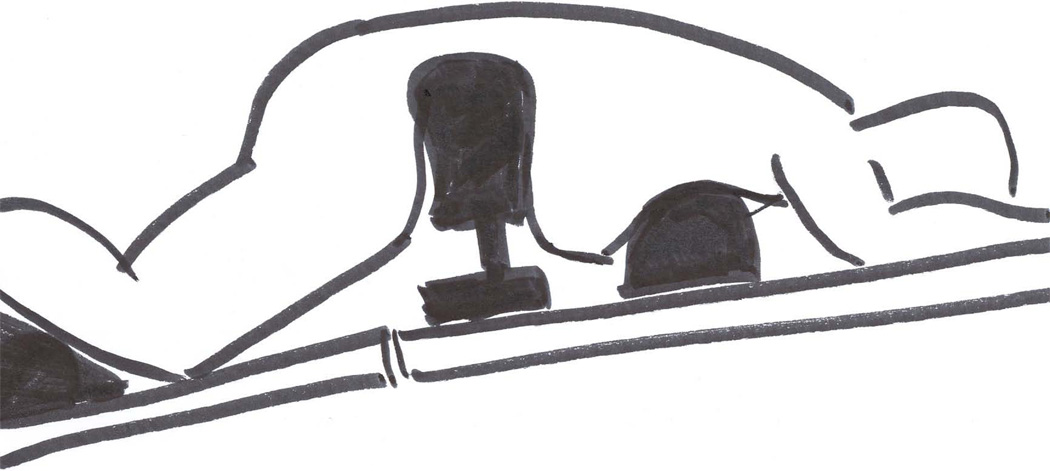
(F). Relton Hall frame. Positioning on the Relton Hall frame: abdomen hangs free, pelvis is supported, legs are positioned below the heart, head is positioned on the foam pillow or headrest; (G) – Relton Hall frame. (Adapted with permission from Relton JE, Hall JE. An operation frame for spinal fusion. A new apparatus designed to reduce hemorrhage during operation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1967, 49(2): 327–32)
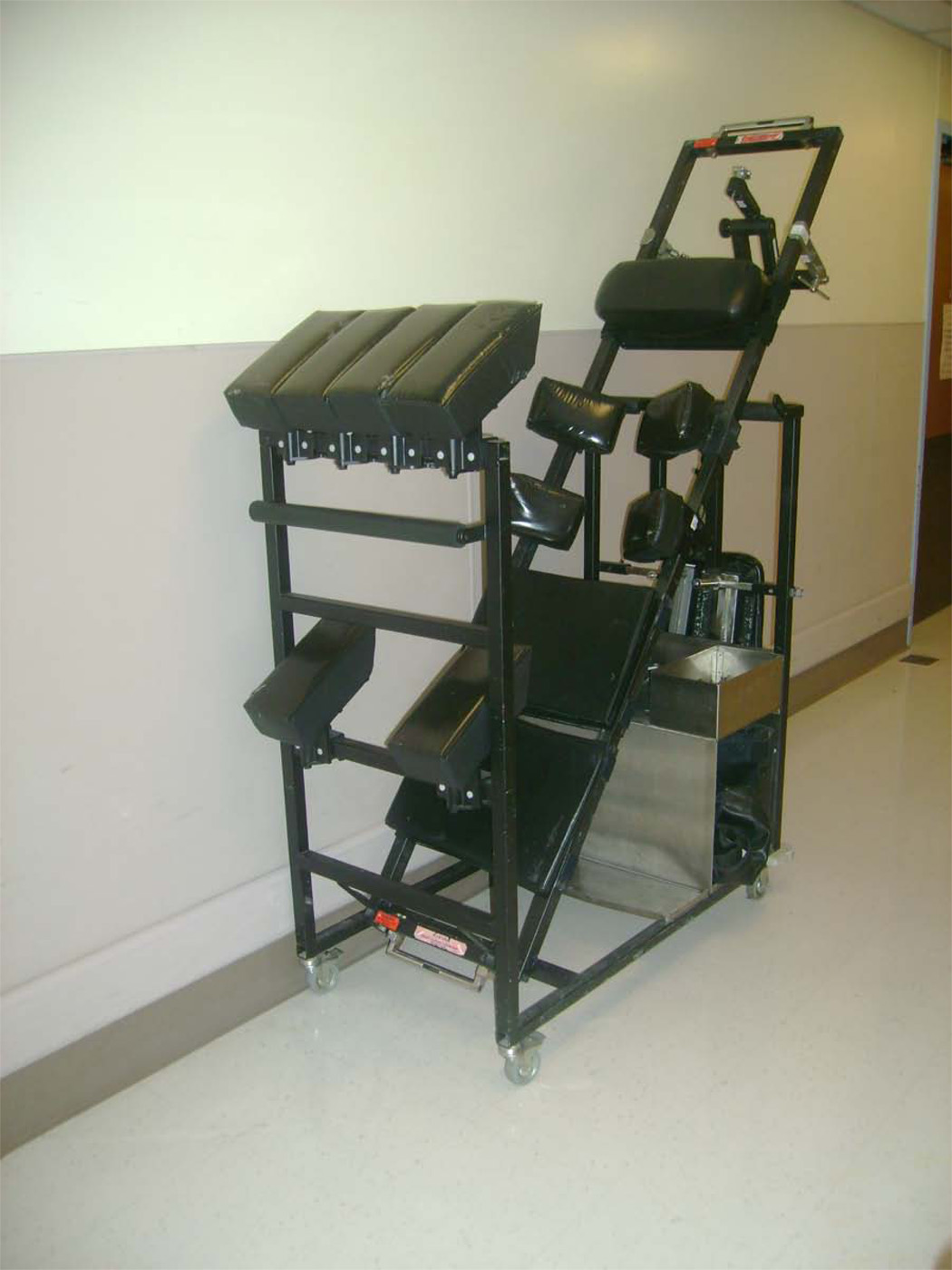
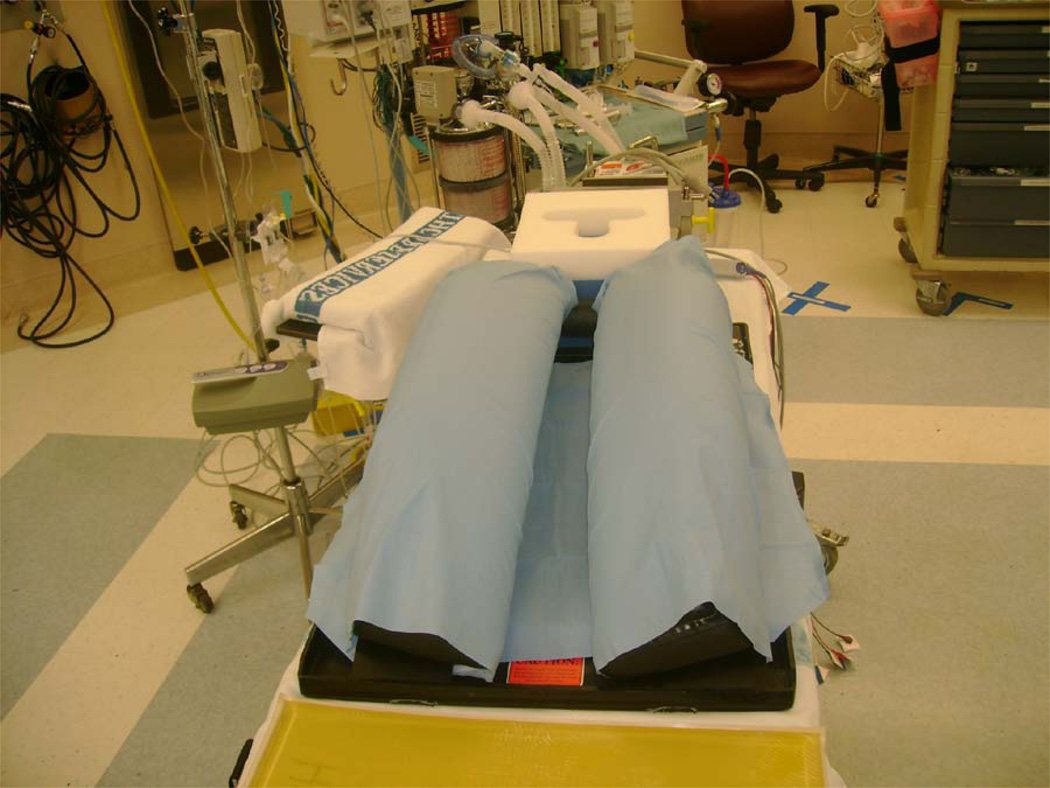
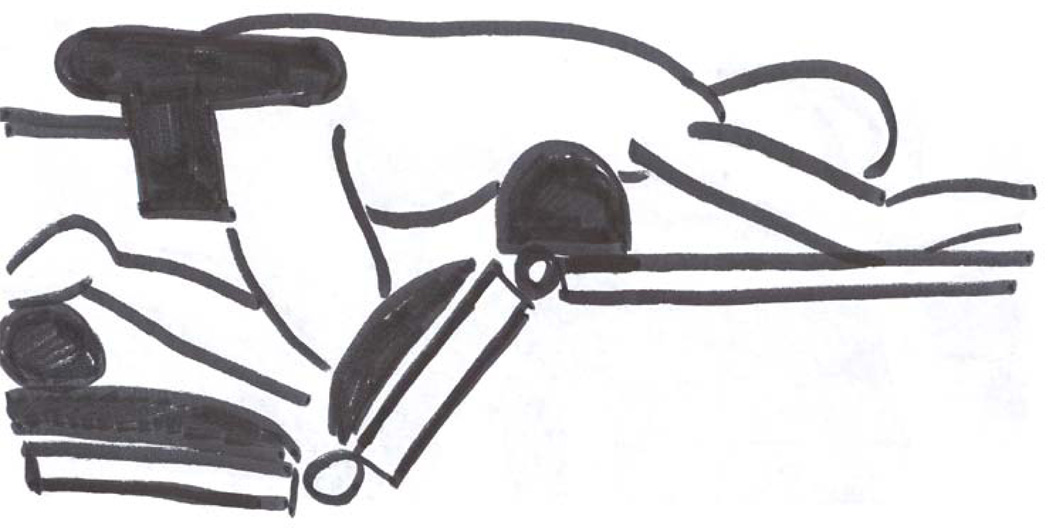
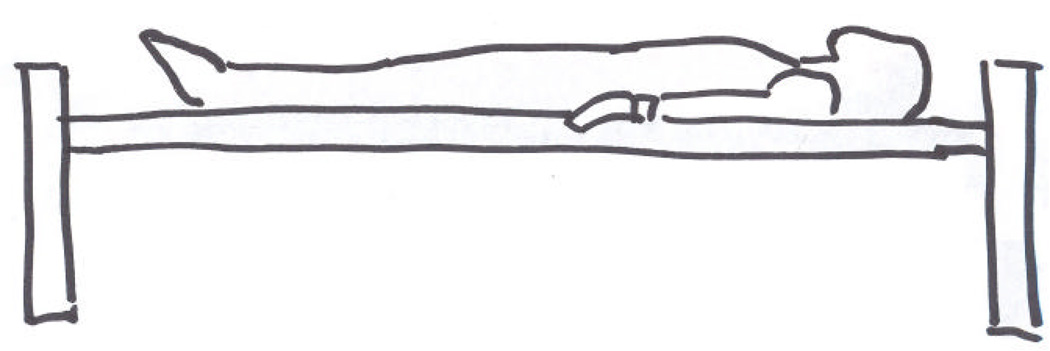
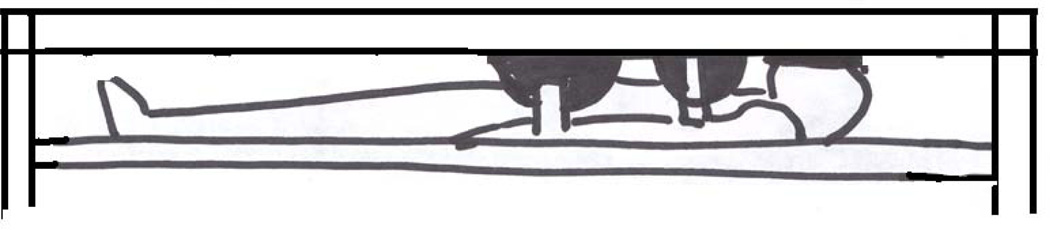
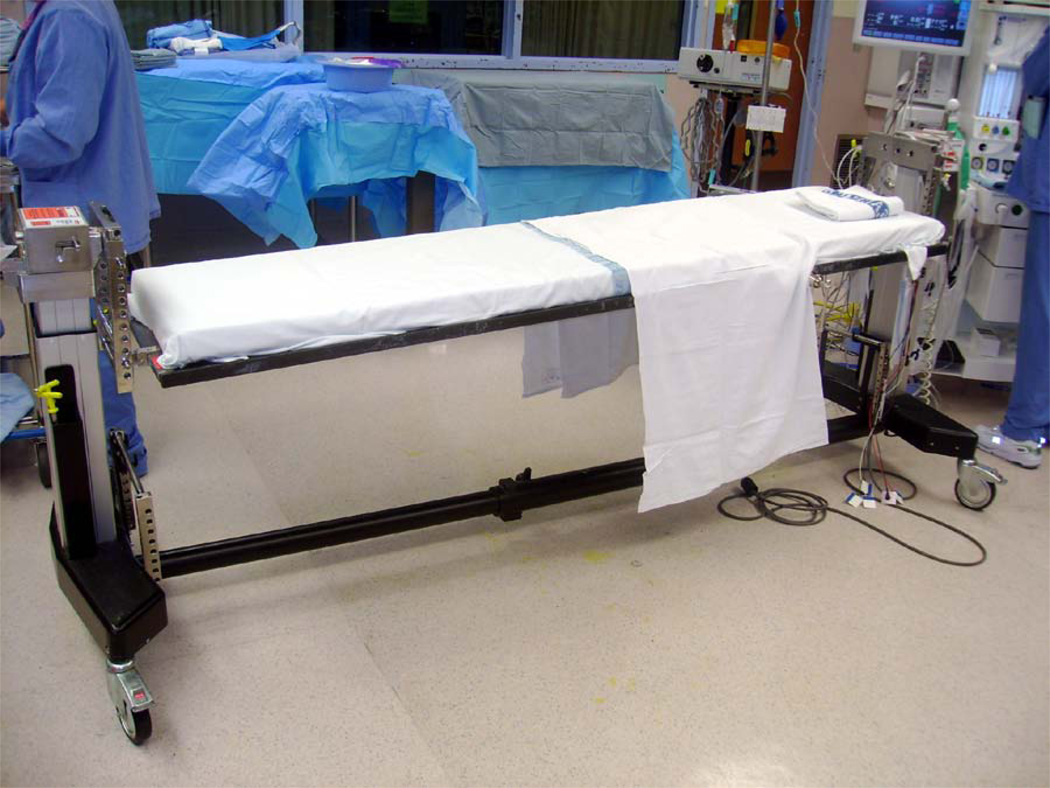
(H). Jackson table. Positioning on the Jackson table: (I) - step I : the patient is lying on the Jackson table, (J) - step II: Jackson frame is put over the patient, the thoracic pad is adjusted to support shoulders and thoracic cage, 2 side pelvic pads are adjusted to the pelvis, and 2 other side pads are adjusted to support the thighs, the patient is compressed between the table and the frame; (K) - step III: after the flipping into prone position has been completed and the Jackson table has been removed from the patients back, the patient is lying on the Jackson frame: abdomen hangs free, pelvis is supported, legs are supported and are positioned at the heart level, head may be positioned on a foam pillow or headrest, or may be fixed with the Mayfield frame; (L) – Jackson table, (M) – Jackson frame.