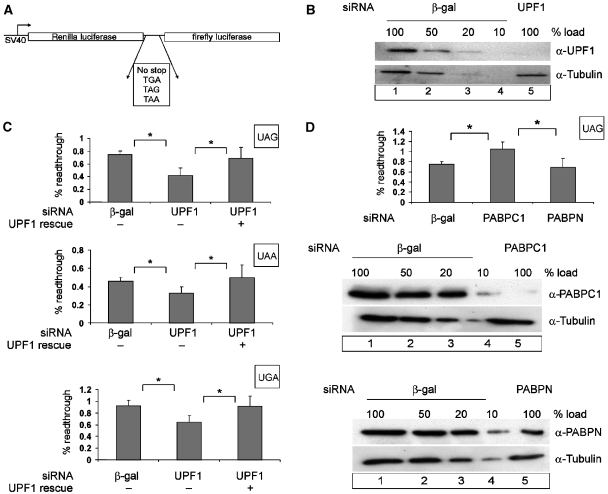
Figure 2.
Effect of UPF1 and PABPC1 on translational readthrough and termination. (A) Schematic representation of the dual luciferase reporters used for measuring translation termination readthrough. (B, C) UPF1 knockdown decreases the level of readthrough at all three stop codons. Protein lysates from HeLa cells that were transfected with siRNAs against β-galactosidase (β-gal) (B, lanes 1–4) or UPF1 (B, lane 5) were immunoblotted with an anti-UPF1 antibody. A dilution series corresponding to 50, 20 and 10% of the protein amount that was used in lane 1 (20 μg) was loaded to assess the efficiency of UPF1 depletion. Reprobing with a tubulin-specific antibody was performed as a loading control. At 48 h after siRNA depletion, HeLa cells were transfected with the dual luciferase construct (p2luc-stop). The percentage of readthrough at the three different stop codons is shown (C). The results obtained with the construct without a stop codon were set as 100% readthrough. To complement the UPF1 depletion, cells were transfected with 0.2 μg of siRNA-resistant FLAG-UPF1R. The values were calculated from six independent depletion experiments, error bars represent standard deviations. *Statistical significance at P<0.05. (D) PABPC1 knockdown increases the level of readthrough at a UAG stop codon. Depletions of PABPC1 and nuclear PABP were achieved by siRNA treatment as described in (B). HeLa cells were transfected with the dual luciferase construct p2luc-TAG or with the construct without an interposed stop codon p2luc-if 48 hours after siRNA treatment. The percentage of readthrough at the UAG stop codon was calculated as described in (C). *Statistical significance at P<0.05.