Fig. 1.
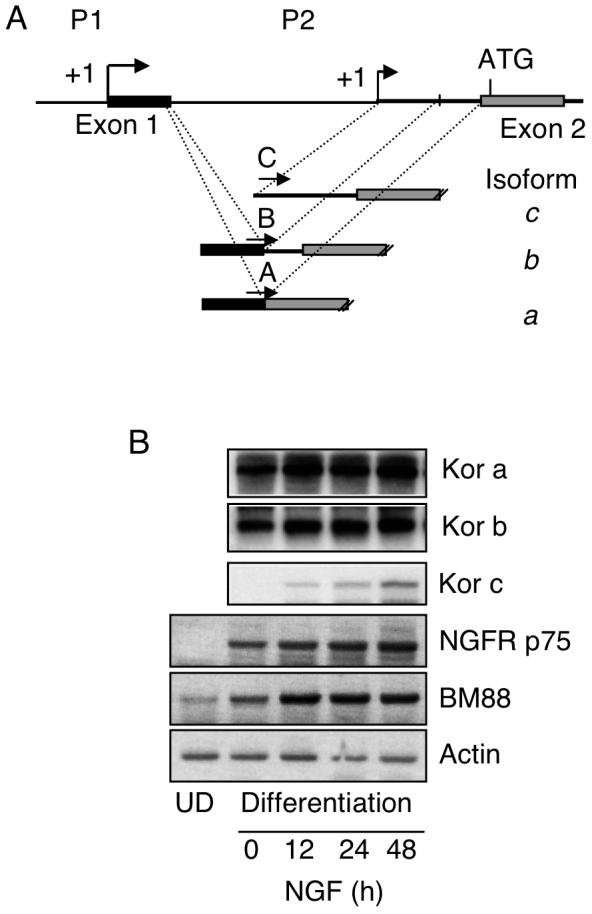
NGF induces expression of KOR c through P2 in RA-induced differentiating P19 cells. (A) The map of KOR gene promoter regions, including P1, P2, exons 1 & 2, and a transcription initiation site of P2 located in intron 1. Splicing variants of P1, isoforms a and b, and P2 transcript isoform c are shown under the map and specific 5′ primers for amplifying each isoform are labeled with A, B and C. The common reverse primer is specific to exon 3. (B) P19 cells were subjected to RA-induced differentiation. After dissociating embryoid bodies and plating onto tissue culture plates, NGF treatment was initiated on day 1 in the absence of RA and cells were harvested on day 3. Isolated RNAs were analyzed by RT-PCR followed by a semi-quantitative Southern blotting procedure using [32P]-probe specific to KOR cDNA (upper left). NGF receptor p75 and neuronal differentiation marker BM88 were also examined on these samples as shown at the bottom. The images shown are the representative of two experiments. UD: Undifferentiated.
