Fig. 5. Effects of wild type and mutant δ-catenin on the dendrogenesis and spine formation in primary hippocampal neurons.
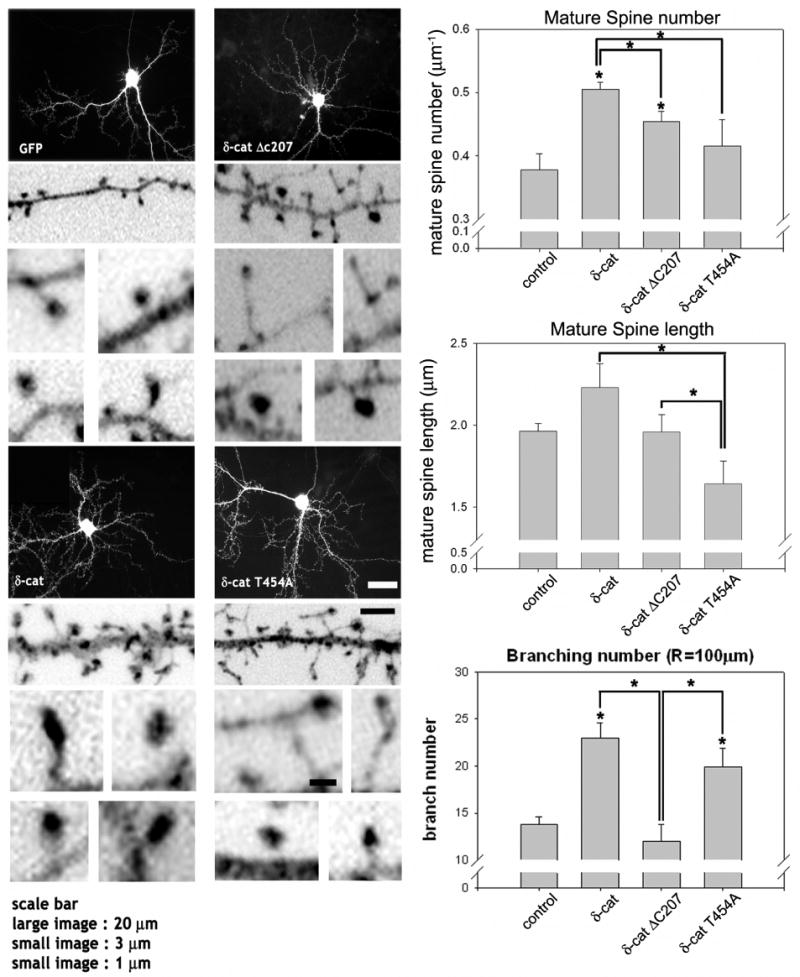
The cultured hippocampal neurons at 16 DIV were transfected with the full-length GFP-δ-catenin or various mutants, fixed and stained with GFP antibody. The high magnification images are inverted for clarity. The average number and length of mature spines, either a cotyloid appearance or flat-apex mushroom appearance, were analyzed and filopodia shaped spines are excluded from analysis (* p<0.01 by ANOVA and Tukey's HSD post hoc test). The number of dendritic branches that intersects a sphere, 100 μm in radius, centered at the soma was added for plotting and statistical analysis using ANOVA and a Tukey's HSD post hoc test. The graphs show the average number of intersections between the dendritic branches and a sphere (* p < 0.01). The study has been repeated with 3 different cultures (3 different litters from 3 different pregnant rats) and from each litter, 3 to 4 coverslips (∼10 neurons per coverslip) have been included in this analysis. Scale bars: 20 μm for low magnification, 3 μm for high magnification, and 1 μm for high magnification of the dendritic spines.
