Fig. 7. δ-Catenin Overexpression decreases the interaction between p190RhoGEF and RhoA.
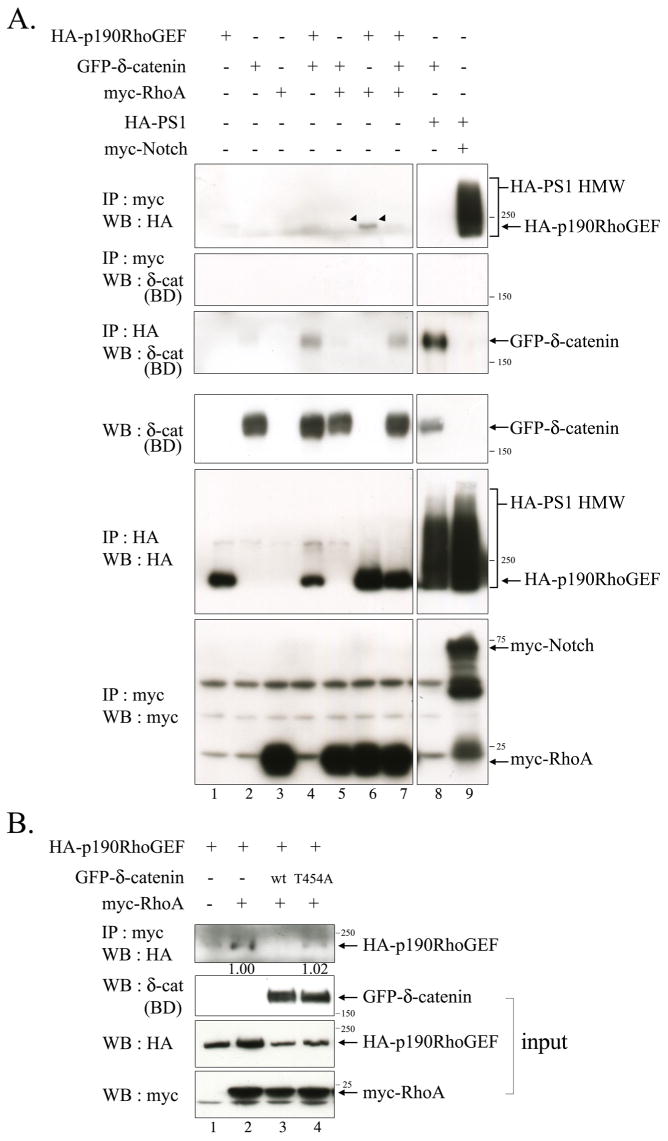
(A) Bosc23 cells were transfected with GFP-δ-catenin, HA-p190RhoGEF, myc-RhoA, HA-PS1 wt, and myc-ΔEN1 in a various combination as indicated in the upper side of the figure. The binding between p190RhoGEF and RhoA was examined by immunoprecipitation with the anti-myc antibody, and western blotting was performed with anti-HA antibody (Upper first panel). The binding between RhoA and δ-catenin was examined by immunoprecipitation with the anti-myc antibody, and western blotting was performed with anti-δ-catenin (BD) antibody (Upper second panel). The bindings between Presenilin-1 with δ-catenin or with Notch were examined for positive control experiments (lane 8, 9 in upper first and third panels). Expression of each protein was shown through the bottom three panels. (B) Bosc23 cells were transfected with either wild type or mutant δ-catenin together with HA-p190RhoGEF and/or myc-RhoA. The binding between p190RhoGEF and RhoA was examined by immunoprecipitation with the anti-myc antibody, and western blotting was performed with anti-HA antibody (Upper first panel). 5% volume of each lysate was subjected to western blot analysis to show the input level of each protein. The relative intensity of the immunoprecipitated HA-p190RhoGEF band in lane 2 vs. 4 was determined by normalization against the input band of HA-p190RhoGEF. 3 μg of each plasmid was used to transfect cells plated in 100 mm dish at 50% confluency.
