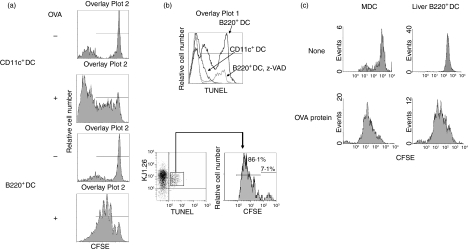
Figure 3.
Liver B220+ DCs stimulate T-cell division and apoptotic death. CFSE-labeled spleen and LN T cells (2 × 105) isolated from DO11.10 (H2d) mice were cultured with irradiated NOD (H2g7) MDCs or liver B220+ DCs in the presence of OVA323−339 peptide (0·3 μm) at DC : T ratio of 1 : 10 for 3 days. Cells were stained with Cy-Chrome-conjugated KJ1.26 mAb and TMR-conjugated TUNEL. (a) CFSE dilution was analysed in a KJ1.26-positive cell population. MDCs and liver B220+ DCs stimulated OVA-specific T-cell division in the presence of OVA peptide. (b) Lower panel: CFSE dilution was analysed in TUNEL+ KJ1.26+ cell population. Majority of apoptotic OVA-specific T cells induced by liver B220+ DCs were dividing cells. Upper panel: in a separate experiment, T cells (2 × 105) from DO11.10 mice were cultured with irradiated NOD MDCs or liver B220+ DCs in the presence of OVA323−339 peptide (0·3 μm) at DC : T ratio of 1 : 10 for 3 days. To inhibit T-cell apoptosis, z-VAD (50 μm/ml, a common caspase inhibitory peptide) was added at the beginning of the culture. Cells were stained with phycoerythrin-conjugated KJ1.26 and fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated TUNEL and analysed by flow cytometry. The histogram showed the intensity of TUNEL in KJ1.26 cells. (c) To ascertain the protein processing and antigen presentation capacity, CFSE-labelled T cells (2 × 105) isolated from DO11.10 mice were cultured with irradiated NOD MDCs or liver B220+ DCs in the presence of OVA protein (200 μg) at a DC : T ratio of 1 : 10 for 3 days. Cells were stained with phycoerythrin-conjugated KJ1.26 mAb. CFSE dilution was analysed in KJ1.26-positive cell population. Liver B220+ DCs could comparably process OVA protein and present antigen to specific CD4+ T cells. The data are representative of three separate experiments.