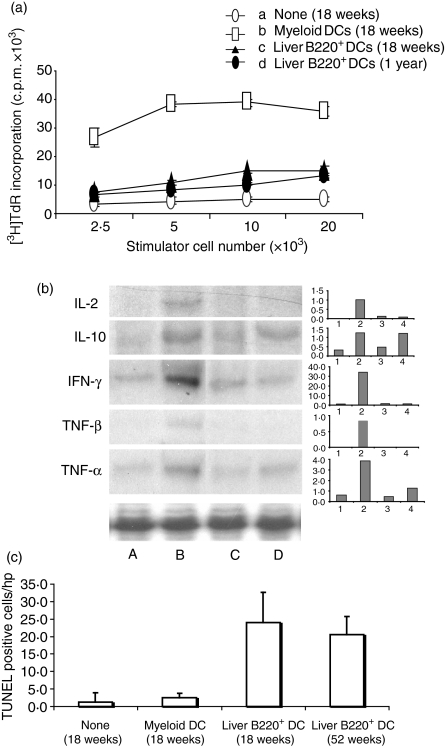
Figure 6.
Administration of liver B220+ DCs into NOD mice induces T-cell hyporesponsiveness to islet antigens. In a 3-day mixed lymphocyte reaction assay, T cells (2 × 105) purified from pancreatic lymph nodes of NOD mice at age of 18 weeks or 1 year that had received 2 × 106 NOD MDCs or liver B220+ DCs at age 7–9 weeks, and used as responders. T cells from NOD DC-untreated or MDC-treated (18 weeks) were used as controls. Graded number of γ-irradiated MDCs from NOD mice pulsed with insulin (10 μg/ml) was used as stimulator. T cells from liver B220+ DC-treated mice showed significantly suppressed proliferative responses (P < 0·05 compared with MDC-treated group). (b) Cytokine mRNA expression (RNase protection assay) in T cells purified from pancreatic lymph nodes of NOD mice that had been treated, at age of 7–9 weeks, with lane A, none; lane B, MDCs (killed at age 18 weeks); lanes C and D, liver B220+ DCs (killed at age of 18 weeks and 1 year, respectively). (c) Administration of liver B220+ DCs enhances apoptosis in pancreatic lymph nodes. Cryostat sections of pancreatic lymph nodes were stained with TUNEL staining in situ. Thirty high-power field of lymph nodes in each mouse were randomly selected and counted for TUNEL-staining-positive cells. The data were collected from three mice in each group, and are presented as positive cell numbers/high-power field ± 1SD. The results are representative of two separate experiments.