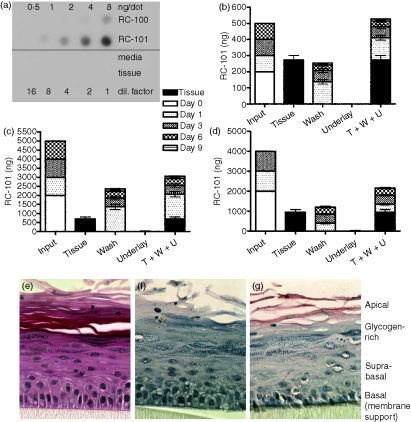
Figure 3.
Topically applied RC-101 is retained within or at the apical surface of vaginal tissues. (a) Quantitative dot blot demonstrating that rabbit polyclonal anti-RC-101 recognized RC-101 peptide but not the tissue maintenance media or untreated vaginal tissue. (b,c) Vaginal tissues were infected (day 0) with HIV-1 BaL in the presence of 200 ng RC-101 in 100 μl PBS (b) or 2000 ng RC-101 in 100 μl PBS (c) and then tissues were washed and re-applied with RC-101 at days 1, 3 and 6 postinfection (Input), as described in the Materials and methods. Collected apical surface wash fluids (Wash, W) and underlay media (Underlay, U), as well as harvested tissues (Tissue, T) were then assayed for RC-101 by dot blot. Values are displayed as stacked bars correlating to harvested tissue or collection day number. (d) Full-thickness vaginal tissues were treated and maintained over 6 days as described in the Materials and methods. Bars represent mean ± SEM, n = 4–6. (e–g) Tissues infected with HIV-1 BaL (25 ng/tissue) and treated with two applications of 400 ng RC-101 (in 50 μl PBS). Tissue sections were subjected to H&E staining (e) and immunohistochemistry with preimmune (f) and anti-RC-101 polyclonal antisera (g) Note the immuno-localization of RC-101 (red stain) primarily in the apical, suprabasal and basal layers.