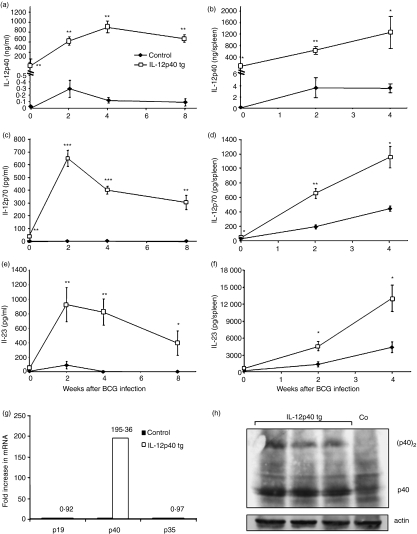
Figure 1.
BCG infection activates transgenic IL-12p40 and results in high concentrations of IL-12p70 and IL-23. Amounts of IL-12p40 (a and b), IL-12p70 (c and d) and IL-23 (e and f) were measured at day 0 and at different time points of BCG infection in IL-12p40 tg mice and control littermates. Cytokines were evaluated in serum (a, c and e) (n = 12–15 mice/group) and in spleen extracts (b, d and f) (n = 5–6 mice/group). Data are represented, in a and b, as means ng of protein per ml of serum or spleen ± SEM or, in c–f, as means pg per serum or spleen. *P < 0·002, **P < 0·00004, ***P < 0·00000002. (g) IL-12p19, IL-12p40, and IL-12p35 mRNA expression in spleen of 2 weeks BCG-infected mice. Relative levels of mRNA were determined by quantitative RT–PCR. Results are expressed as fold increase in IL-12 subunit mRNA expression in IL-12p40 tg mice as compared to non-transgenic mice (n = 3 mice/group). (h) Identification of homodimeric (p40)2 and monomeric p40 in spleen of IL-12p40 tg mice at 4 weeks of BCG infection by Western blot. Only the monomeric form p40 is detected in non-transgenic mice. Spleen proteins were also blotted with an anti-actin antibody as control for protein loading. These results are representative of two or three independent experiments.