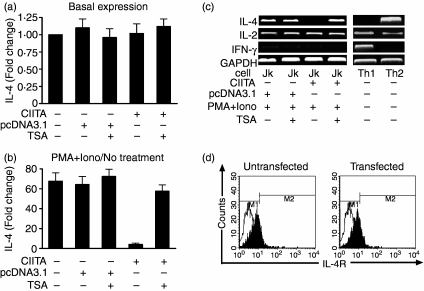
Figure 2.
Suppressed expression of IL-4 in CIITA-transfected Jurkat cells. (a) There was no difference in basal IL-4 expression in the different groups of Jurkat cells without PMA + Iono stimulation. Fold changes were calculated by comparing the amount of IL-4 mRNA in the different groups with that of wild-type cells followed by normalization to GAPDH levels. The amount of IL-4 mRNA in wild-type cells without TSA treatment was designated as 1·0 (see bar 1). (b) Determination of the suppressed expressions of IL-4 by real-time PCR in the Jurkat cells stimulated with PMA plus ionomycin. Fold changes of transcription in each group were calculated by comparing IL-4 expression in (PMA + Iono)-stimulated cells with that of unstimulated cells (no treatment) followed by normalization to GAPDH levels. The amount of IL-4 mRNA in unstimulated cells of each group was designated as ‘1·0’. Treatment with TSA reversed the CIITA-related suppression of IL-4 expression. (c) The expression of IL-4, instead of IL-2, is almost completely inhibited in the CIITA-transfected Jurkat cells stimulated by PMA plus ionomycin as determined by RT-PCR. The depression can be reversed by TSA, an inhibitor of histone acetyltransferase. Th1 and Th2 cells were used as controls. (d) No change in percentages for IL-4R-positive Jurkat cells (around 20%) before (left) and after (right) transfection with the CIITA gene, suggesting no functional involvement of IL-4R in the CIITA-related suppression of IL-4. Black and white peaks stand for the negative control and the IL-4R-positive cells, respectively.