FIGURE 6. Identification and structural characterization of synthetic, plasma and red blood cell OA-NO2 by HPLC ESI MS/MS.
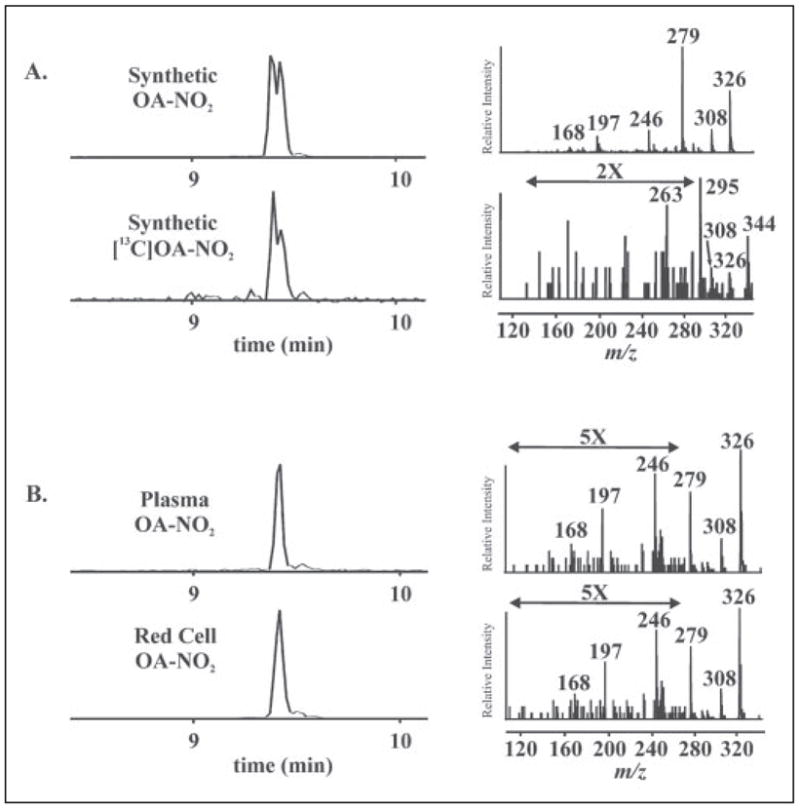
A: left panels, OA-NO2 and [13C18]OA-NO2 were characterized by HPLC ESI MS/MS in the negative ion mode. Nitrated oleic acid species were separated by HPLC and detected by acquiring MRM transitions consistent with the loss of the nitro functional group [M-HNO2]−: m/z 326/279 and m/z 344/297 for OA-NO2 and [13C18]OA-NO2, respectively. Right panels, concurrent to MRM detection, product ion analysis was performed to generate the identifying fragmentation patterns used to characterize OA-NO2 present in red cells and plasma. The predominant product ions generated by collision-induced dissociation are identified in TABLE TWO. B, total lipid extracts were prepared from packed red cell and plasma fractions of venous blood and directly analyzed by HPLC ESI MS/MS.
