Figure 6.
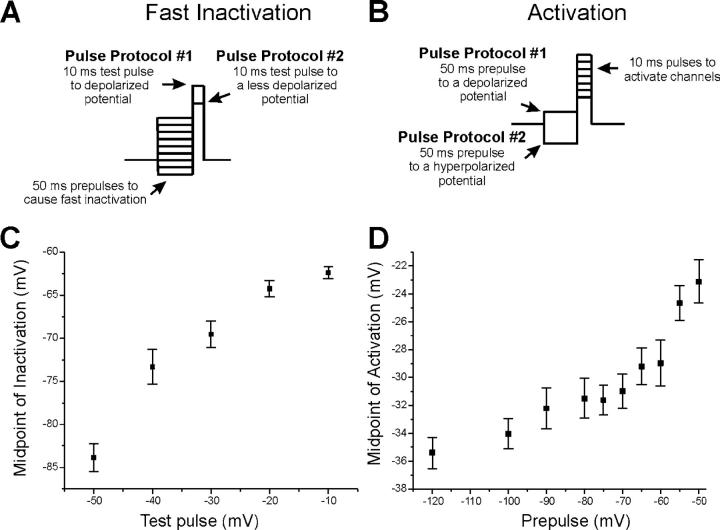
The measured voltage dependence of sodium channel inactivation and activation depends on the pulse protocol used. (A) Examples of two pulse protocols used to measure the voltage dependence of fast inactivation. In protocol 1, a depolarized test potential is used that activates all sodium channels. Thus when prepulses are altered to measure the voltage dependence of fast inactivation, the measured voltage dependence of fast inactivation is affected by all Nav1.4 sodium channels. In protocol 2, a more hyperpolarized activation pulse is used that only activates channels that gate at hyperpolarized potentials. In protocol 2, the voltage dependence of inactivation will preferentially measure the voltage dependence of inactivation of sodium channels that have a hyperpolarized voltage dependence of activation. (B) Examples of two pulse protocols used to measure the voltage dependence of activation. In protocol 1, a depolarized prepulse preferentially inactivates sodium channels that inactivate at hyperpolarized potentials. Thus protocol 1 will preferentially measure the voltage dependence of activation of sodium channels that have a depolarized voltage dependence of inactivation. Protocol 2 will not inactivate any sodium channels so that the voltage dependence of activation includes both sodium channels that inactivate at hyperpolarized potentials and sodium channels that inactivate at depolarized potentials. (C) The midpoint of inactivation is plotted against the test pulse used to activate sodium channels in a patch held at −80 mV. Use of a test pulse of −50 mV yields a midpoint of inactivation of close to −84 mV. Use of more depolarized test pulses yielded more depolarized midpoints of inactivation. (D) The midpoint of activation is plotted against the prepulse potential used to inactivate sodium channels before measurement of the voltage dependence of activation in a patch held at −80 mV. As the prepulse becomes increasingly depolarized, the measured voltage dependence of activation shifts toward depolarized potentials. For inactivation, n for each test potential is (−50:5, −40:9, −30:13, −20:10, −10:12). For activation, n for each prepulse is (−120:9, −100:10, −90:7, −80:7, −75:10, −70:8, −65:8, −60:8, −55:9, −50:9).