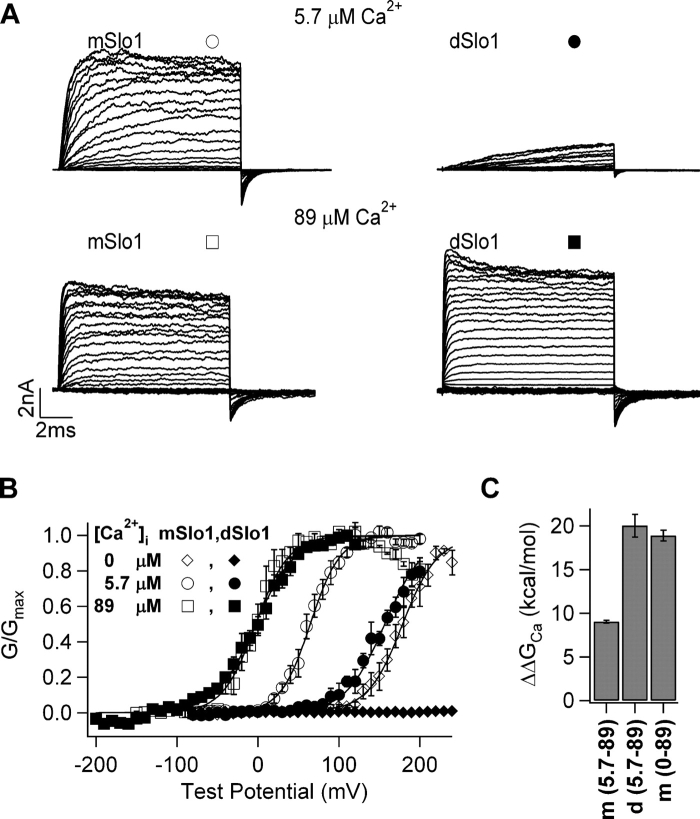
Figure 1.
dSlo1 activation exhibits higher Ca2+ sensitivity than mSlo1. (A) Current traces of mSlo1 and dSlo1. Test potentials were −80 to +200 mV and −150 to +200 mV for 5.7 μM and 89 μM [Ca2+]i, respectively, holding and repolarization potentials were −50 mV. (B) Steady-state G-V relations of mSlo1 and dSlo1. Smooth curves are fits of the Boltzmann equation (see MATERIALS AND METHODS) with parameters for mSlo1, in 0 [Ca2+]i: V1/2 = 179 mV, z = 1.2, in 5.7 μM [Ca2+]i, V1/2 = 64.6 mV, z = 1.4, in 89 μM [Ca2+]i, V1/2 = −2.8 mV, z = 1.2; for dSlo1, in 5.7 μM [Ca2+]i, V1/2 = 157 mV, z = 1.3, in 89 μM [Ca2+]i, V1/2 = −2.9 mV, z = 1.1. (C) Free energy provided by Ca2+ binding for channel activation when [Ca2+]i changes from 0 or 5.7 μM to 89 μM, as indicated in parentheses under the abscissa. m, mSlo1; d, dSlo1.