Figure 2.
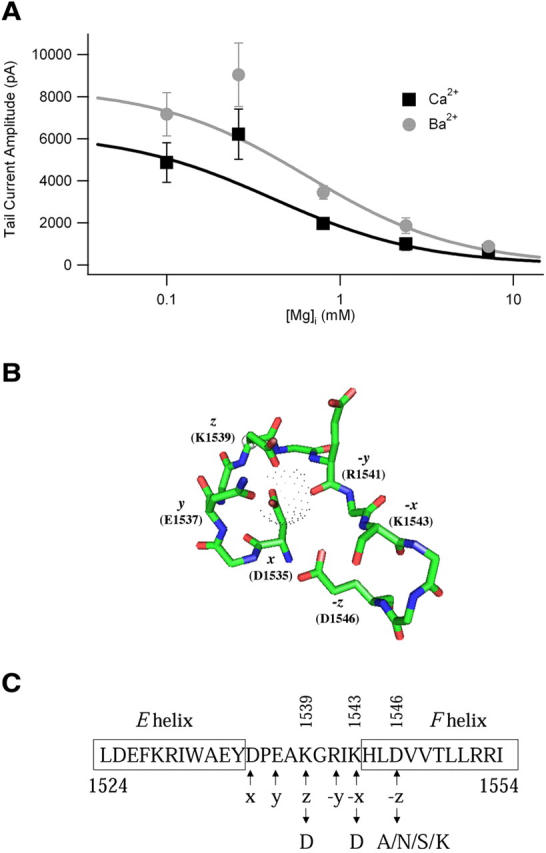
The COOH-terminal EF-hand motif as a possible Mg2+ binding site. (A) Effect of Mg2+ on IBa and ICa through Cav1.2 channels. Comparison of Mgi effects on WT channels using 10 mM Ba2+ or 1.8 mM Ca2+ as the charge carrier. Plot of mean tail current amplitude following test pulses to +80 mV versus Mgi concentration. The data were fit using a single binding site model. The fit curves are binding isotherms obtained with a global fitting procedure implemented in Igor Pro assuming a common coefficient for the number of binding sites (Hill coefficient). Using this procedure gave a Hill coefficient of 0.77 with 95% confidence limits of ±0.16 and an apparent Kd value for inhibition by Mgi of 0.65 mM (WT). (B) EF-hand motif of CaV1.2. Model of binding of Mg2+ to the EF-hand of CaV1.2 illustrating the ion-coordinating residues in a Mg2+-bound EF-hand using the structure of the COOH-terminal EF hand of Mg2+-calbindin (PDB 1IG5) with the CaV1.2 amino acid residues substituted on it. Amino acid side chain oxygens serve as direct ligands of the bound Mg2+ for the positions x, y, z, and −z. The ligand at the −y position is donated by the backbone carbonyl oxygen of R1541, and the ligand at the −x position is the oxygen atom of an H2O bound to K1543 (not depicted). The Mg2+ ion is represented by a dot surface. Sequence numbers identified below each ligand position denote the corresponding residues in CaV1.2. (C) Amino acid sequence of the EF-hand of CaV1.2 and the mutations made at each position.
