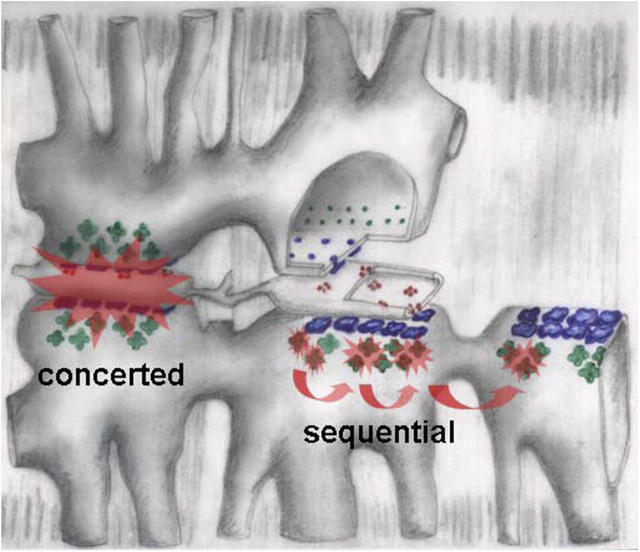
Figure 6.
Hypothetical mechanisms of two activation patterns in frog fibers. Triads are drawn progressively separated and stripped of components from left to right. α channels, in blue, are grouped in couplons that face the junctional gap. They undergo concerted activation, pictured as a Ca2+-mediated interaction that propagates very rapidly in the narrow gap, then stops at the edges of the couplon. Sequential activation is attributed to β channels (green), facing the wide parajunctional space. Ca2+-mediated activation there should propagate more slowly, but freely, without defined structural bounds. “Mixed” events are not excluded in this view.