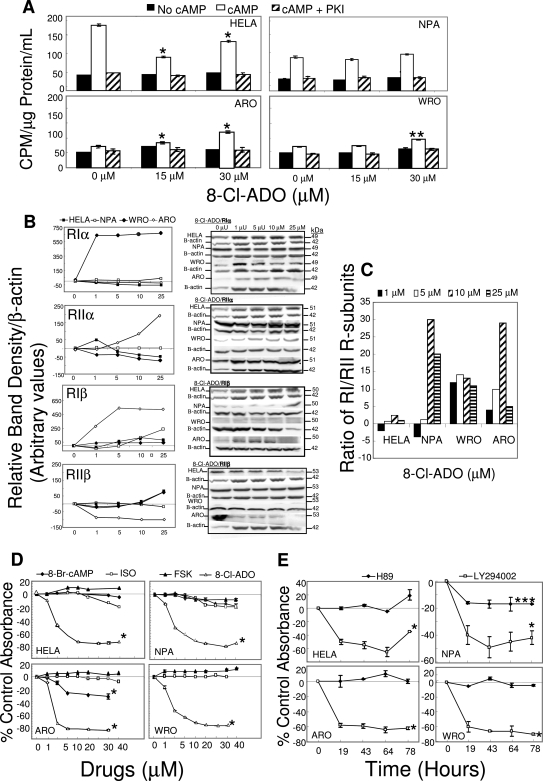
Figure 5.
Differential effect of 8-Cl-ADO on PKA activity in thyroid cancer cells and in HeLa cells: no significant effect of PKA pathway stimulants or the PKA activity inhibitor H89 on cell metabolism/proliferation. A, Cells in 175-cm2 flasks were incubated with 8-Cl-ADO (15 and 30 μm) for 4 d, and cell extracts were exposed to cAMP or to cAMP plus the PKA-specific inhibitor PKI. PKA activity levels were then determined. Results are expressed as cpm [γ32P]dATP per microgram protein per milliliter and are mean ± sem of three experiments. B, Cells in 175-cm2 flasks were incubated with 8-Cl-ADO (0–25 μm) for 4 d and lysed, and gel electrophoresis and immunoblot assay were performed using antibodies to PKA R-subunits. C, Ratio of PKA R-subunits RIα plus RIβ/ RIIα plus RIIβ from B above. D, Cells in 96-well culture plates were incubated for 4 d with increasing concentrations (0–40 μm) of the PKA pathway stimulants 8-Br-cAMP, isoproterenol (ISO), and forskolin (FSK), or with 8-Cl-ADO. E, cells were incubated with the PKA pathway inhibitor, H89 (50 nm) or with the PKB (Akt)-pathway inhibitor LY294002 (30 μm) for 0–78 h. Cell titer 96 AQ solution was added to cultures in D and E for 3.5 h, before plates were read using an ELISA plate reader at 460 nm. Points in B are mean ± sem of three experiments, expressed as percentage of control band density/Β-actin (arbitrary values). Bands are representative of one experiment. Results are expressed as percentage of control absorbance ± sem of three experiments (D) or mean ± sd of two experiments (E). *, P < 0.0001 (A, D, and E); **, P = 0.0005 (A); ***, P = 0.01 (E) compared with baseline.