Table 1. Expected Traveling Time of Different Means of Signaling. (Calculated for 40 µm synapse-to-nucleus distance, which correspond to ∼30* µm synapse-to-soma distance).
| Means | Speed | Time | References |
| Transport vesicles | 11–21 µm/hr | 2–4 hr | [14] |
| Transport granules** | 122 µm/hr | 20 min | [15] |
| Diffusion of CaM | D = 2.5×10−9 cm2/s | 48 min | [8] |
| Diffusion of kinase-bound CaM | D = 5×10−8 cm2/s | 2.7 min | [8] |
| Regenerative Calcium waves*** | ∼0.1 µm/ms | 0.4 sec | [16] |
| Electrotonic signal | 81 µm/ms | 0.5 ms | **** |
*: The distance from the soma to the most proximal spine was reported to be 39.7±12.1 µm [9].
**: Average maximal speed of granules traveling along a dendrite is 0.034±0.025 µm/s [15].
***: Regenerative Calcium waves were ruled out as means for synapse-to-CREB signaling [1].
****: Electrotonic speed (θ) was calculated according to the parameters in Table 2 using the conventional definition 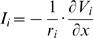 given by the classic cable theory.
given by the classic cable theory.
