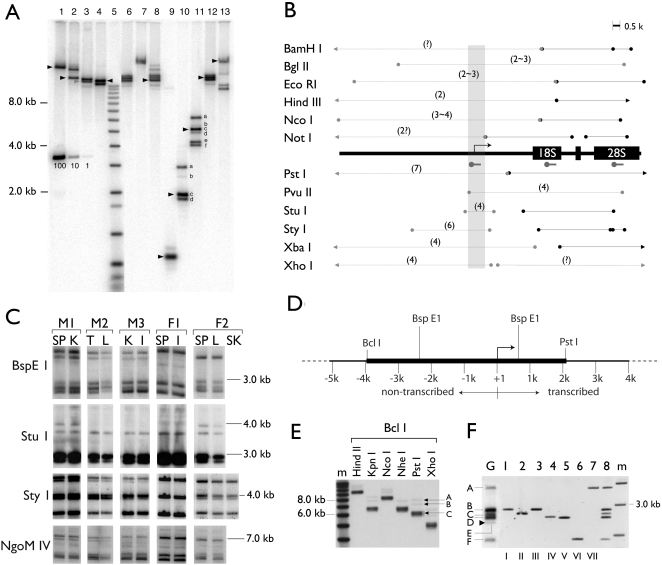
Figure 1. Molecular cloning of rDNA variants from CF1 mouse.
A, An example of rDNA RFLPs revealed by Southern analyses of CF1 liver genomic DNA. The Southern blot was probed with a DNA fragment from the promoter-leader region of rDNA. A molecular weight marker (mw) is included (lane 5) and the molecular weights indicated to the left. Bands of size predicted by the published rDNA sequence (BX000964) are indicated by arrowheads. A serial copy number marker is indicated by the copy numbers each band contains (i.e., 100, 10, 1). The copy number was calculated as described in Tian et al., 2001, using 2.7×109 bp for the haploid mouse genome. The fragments, whose copy numbers were assessed and described in the text, are alphabetically labeled (lanes 10 and 11). The restriction enzymes used to generate A are the most informative among the thirty enzymes tested. They are listed as they appear in B (i.e., lane 1, BamHI, lane 2, Bgl II, with the exception of lane 5). B, A summary of the RFLPs detected by the Southern analyses. A generic rDNA (partial) is depicted in the middle, with transcription start site (bent arrow), the coding sequence (18S and 28S) and the hybridization probe (hammers) indicated. The polymorphism or lack thereof is depicted by circle-ended grey lines and black lines, respectively. The number of polymorphisms for a given restriction fragment is shown in parentheses. The gray area indicates the variable region around the transcription start site. C, The promoter region RFLP is stable during organ development. Genomic DNA was isolated from tissues of five unrelated mice, three males (M1, 2 and 3) and two females (F1 and 2) and analyzed by Southern blots. Tissue genomic DNAs were digested with one of the four enzymes (Bsp E1, Stu I, Sty I and NgoM IV) as indicated to the left of the gel image. The blots were probed with the same rDNA promoter fragment as shown in A. SP, spleen, K, kidney, T, testis, L, liver, I, intestine, SK, skin. Note that no variation is detected among the tissues of an individual. D, A restriction map indicates the cutting sites of relevant enzymes. The thicker line depicts the target fragment for cloning. The indicated size (∼6 kb) is that predicted by the published sequence. E, Liver genomic DNA was double-digested with Bcl I and another restriction enzyme and probed with the promoter-leader probe. Bcl I-Pst I digestion yielded three groups of bands, which were purified individually by size-fractionation and used to generate libraries designated A, B and C, respectively. F, Seven variant rDNAs (v-rDNA) were cloned and each contained an internal BspE1 fragment (lanes 1 to 7) that matched a BspE1 RFLP of the genomic DNA (lane G). When mixed as a group, the BspE1 digestion pattern of these v-rDNA clones (lane 8) resembles that of the genomic digestion (lane G). Note one v-rDNA RFLP was not isolated (band E, arrow head in lane G).