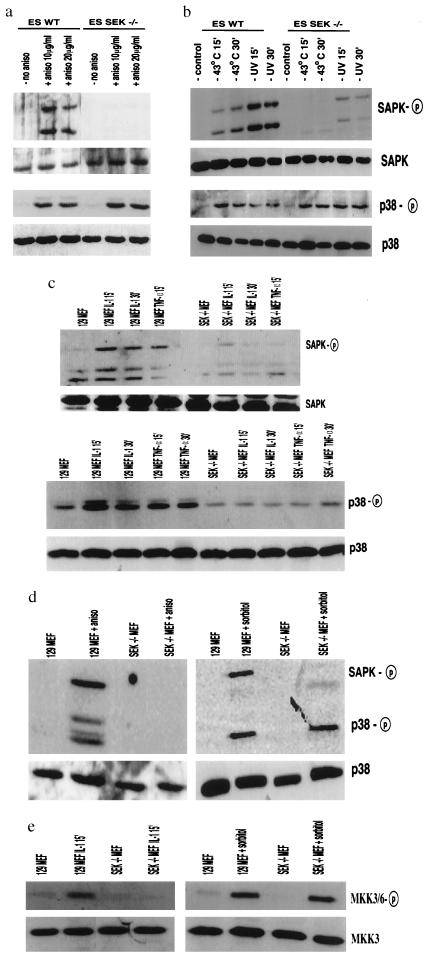
Figure 2.
Effect of SEK1 gene disruption on the phosphorylation and activation SAPK/JNK and p38 in ES cells and mouse embryonic fibroblasts. (a) Western blot analysis of wild type (ES WT) and SEK1−/− (ES SEK−/−) ES cells either untreated or activated with anisomycin (10 and 20 μg/ml, 30 min). Western blots were probed with specific antisera to phospho SAPK/JNK and p38. Control Western blots for levels of SAPK and p38 protein also are shown. (b) Wild-type (ES WT) and SEK1−/− (ES SEK−/−) ES cells were either untreated or UV treated (80 J/m2 and then incubated for 15 min, 30 min) or heat shocked (43°C, 15 min, 30 min). Western blot analysis for phospho SAPK/JNK and phospho p38 is shown. Control Western blots for levels of SAPK and p38 protein also are shown. (c) 129 MEFs and SEK1−/− MEFs were stimulated with IL-1 (10 ng/ml, 15 min and 30 min) or TNFα (50 ng/ml, 15 min). Western blot analysis for phospho SAPK/JNK and phospho p38 is shown. Control western blots for levels of SAPK and p38 protein also are shown. (d) 129 MEFs and SEK1−/− MEFs stimulated with anisomycin (40 μg/ml, 30 min.) and sorbitol (2.5 mM, 15 min). Western blot analysis for phospho SAPK/JNK and phospho p38 is shown. Control Western blots for levels of SAPK and p38 protein also are shown. (e) 129 MEFs and SEK1−/− MEFs stimulated with IL-1 (10 ng/ml, 15 min) or sorbitol (2.5 mM, 15 min). Western blot analysis for phospho MKK3/6 is shown. Control Western blots for levels of MKK3 protein also are shown.