Fig. 6.
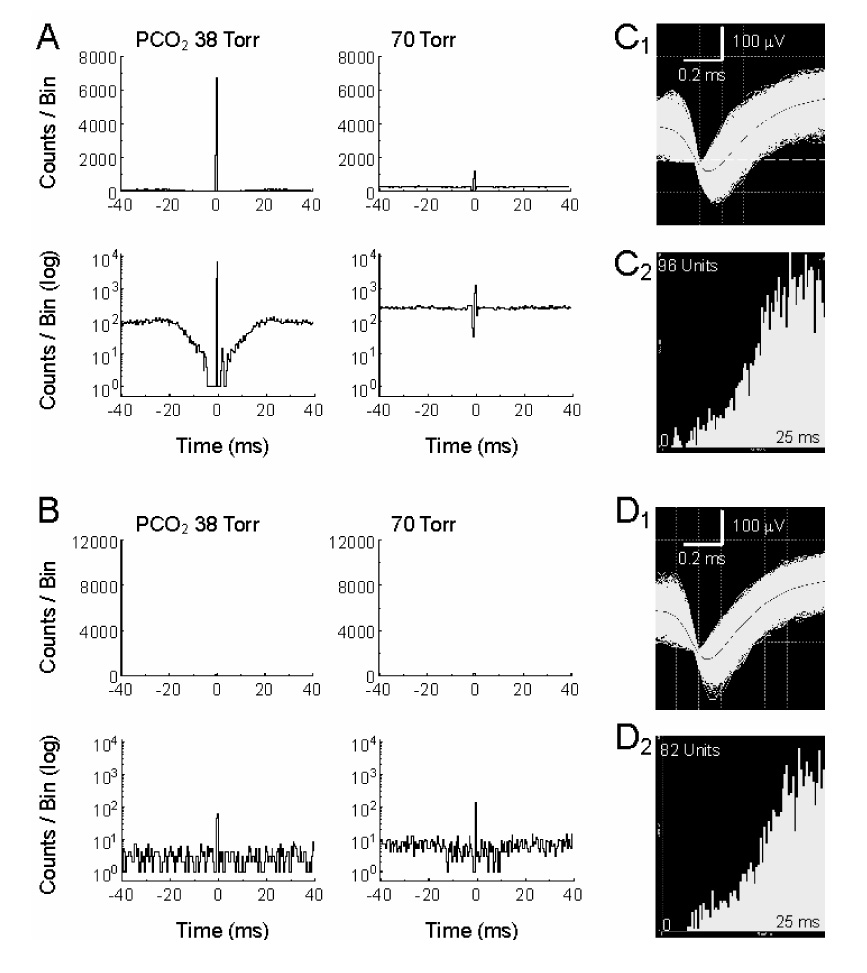
Sensitivity of the electrical coupling to halothane. A. Electrical coupling was seen in a pair of CO2-stimulated units (coupling efficiency = 0.91). The electrical coupling was strongly and reversibly inhibited with hypercapnia (coupling efficiency = 0.17). B. The electrical coupling was also strongly inhibited by 2mM halothane (coupling efficiency = 0.18). In the presence of halothane, hypercapnia failed to inhibit the electrical coupling (coupling efficiency = 0.21). C, D. Action potential morphology and interspike internal analyses indicate that these units are single and recorded from soma.
